We at Durham Guild Equity Research are initiating coverage on AMD (Advanced Micro Devices), a leading technology company known for its microprocessors and GPUs. This report is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as an investment recommendation.
About the Business
Since its founding in 1969, AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) has been a pioneer in the semiconductor industry. The company’s innovative microprocessors and GPUs have greatly advanced computing performance, fueling the growth of the PC gaming market and powering data centres. AMD’s cutting-edge technologies are now essential to modern AI, high-performance computing, and various industries, making it a key player in the digital transformation of markets worldwide.
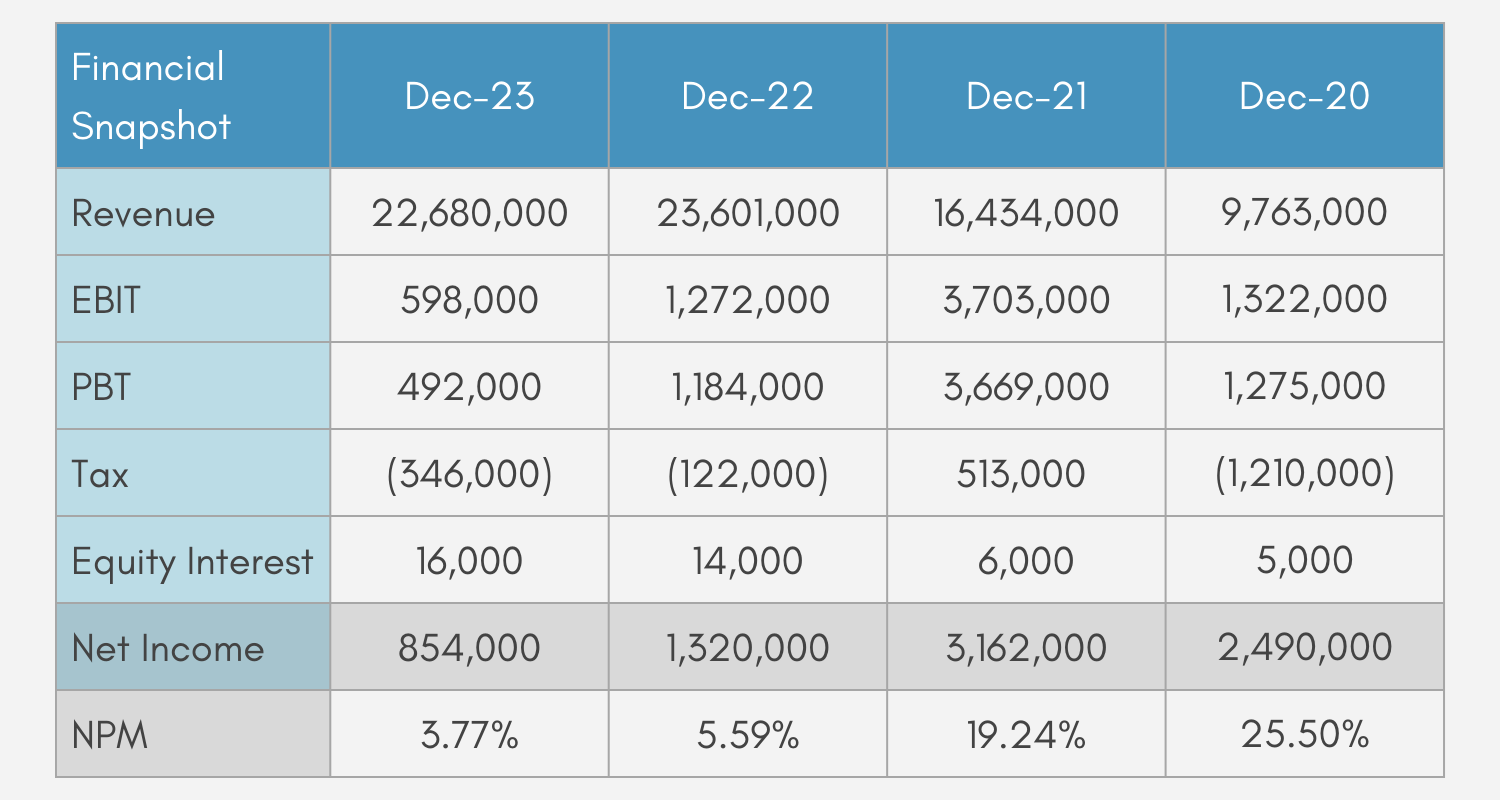
All figures in thousands USD for the fiscal years ended:
Key Points About the Company
- AMD surpassed analyst expectations in its latest financial report, revealing fourth-quarter earnings of $6.6 billion in revenue and $0.85 in earnings per share. Since its founding in 1969, AMD (NASDAQ: AMD) has been a pioneer in the semiconductor industry. The company’s innovative microprocessors and GPUs have greatly advanced computing
performance, fueling the growth of the PC gaming market and powering data centres. AMD’s cutting-edge technologies are now essential to modern AI, high-performance computing, and various industries, making it a key player in the digital transformation of markets worldwide. - The company witnessed remarkable growth in its data center revenue, up by more than 150% compared to the same period last year, reaching $3.2 billion.
- AMD is gearing up to release its highly anticipated Ryzen 8000 series chip in 2024, generating excitement for its future growth. Collaborating with Microsoft, AMD aims to develop AI solutions
to enhance cloud computing infrastructure. - With its stock price more than doubling over the past year, AMD’s market valuation has exceeded $200 billion, firmly establishing itself among top-tier tech giants.
- AMD hit an all-time high in its stock price on March 1, reaching $159.67, with an average stock price over the last 52 weeks of $98.35.
- AMD has a substantial float, with approximately 71.34% of its shares held by institutional investors. This high level of
institutional ownership contributes to the liquidity of the stock. - Holding a 16% market share in the GPU market, AMD’s graphics processing units significantly contribute to its overall profitability.
Float and Major Shareholders
- AMD has a substantial float, with approximately 71.34% of its shares held by institutional investors. This high level of
institutional ownership contributes to the liquidity of the stock. - AMD’s major shareholders include significant institutional investors, reflecting strong market confidence. Vanguard Group Inc. is the largest shareholder with holdings valued at $26.13 billion. Other major investors include Aspire Private Capital LLC with $12.06 billion, BlackRock Inc. with $7.46 billion, State Street Corp with $7.43 billion, and Jennison Associates LLC with $4.37 billion. These institutions collectively hold a substantial portion of AMD’s shares, providing stability and influencing market dynamics due to their significant ownership stakes.
Quarterly Performance
Segment Performance
- Data Center: Achieved $2.3 billion in revenue (up 80% year-over-year), buoyed by strong demand for AMD Instinct GPUs and EPYC CPUs.
- Client Segment: Revenue was $1.4 billion (up 85% year-over-year), driven by new Ryzen processor launches.
- Gaming Segment: Revenue was $922 million (down 48% year-over-year), showing stability despite a seasonal decline.
- Embedded Segment: Performance remained robust with growing adoption in automotive and industrial applications, however was down $846 million (46% year-over-year).
Other Information
- Product Launches: Introduced the Ryzen 8000 series processors and Radeon RX 7600 XT GPU.
- Data Center: Achieved $2.3 billion in revenue (up 80% year-over-year), buoyed by strong demand for AMD Instinct GPUs and EPYC CPUs.
- Client Segment: Revenue was $1.4 billion (up 85% year-over-year), driven by new Ryzen processor launches.
- Gaming Segment: Revenue was $922 million (down 48% year-over-year), showing stability despite a seasonal decline.
- Embedded Segment: Performance remained robust with growing adoption in automotive and industrial applications, however was down $846 million (46% year-over-year).
- Supercomputing: AMD technology powers 140 of the top supercomputers, including the world’s fastest, the Frontier.
- Microsoft: Partnered to enhance AI and cloud services with AMD Instinct MI300X accelerators and EPYC CPUs.
- Eni: Developed the HPC6 supercomputer powered by AMD EPYC CPUs and Instinct GPUs for industrial applications.
- Automotive Sector: Introduced Versal AI Edge XA Series and Ryzen Embedded V2000A devices for advanced driver safety, autonomous driving, and infotainment.
Future Outlook
- Revenue: Expected to be approximately $5.7 billion, plus or minus $300 million, representing about 6% year-over-year
growth and 4% sequential growth. - Non-GAAP Gross Margin: Projected to be around 53%, reflecting ongoing improvements in cost efficiency.
- Data Center Revenue: Anticipated to remain flat sequentially, with a seasonal decline in server sales offset by strong
data center GPU growth. - Client, Embedded, and Gaming Segments: Expected to decline sequentially due to seasonal factors, with a significant double-digit percentage decline in semi-custom revenue.
Conclusion
The quarterly performance data presents a mixed picture for the company, highlighting both significant gains and notable declines across various segments. The Data Center segment saw impressive revenue growth, reaching $2.3 billion, an 80% increase year-over-year, driven by robust demand for AMD Instinct GPUs and EPYC CPUs. Similarly, the Client segment experienced substantial growth, with revenue up 85% to $1.4 billion, propelled by new Ryzen processor launches. However, the Gaming segment faced a sharp decline, with revenue dropping 48% year-over-year to $922 million, although it managed to maintain stability despite seasonal fluctuations. The Embedded segment showed resilience with continued adoption in automotive and industrial applications, yet its revenue decreased by 46%, amounting to an $846 million decline year-over-year. Other noteworthy developments include the introduction of the Ryzen 8000 series processors and the Radeon RX 7600 XT GPU, and AMD’s significant presence in the supercomputing sector, powering 140 of the top supercomputers, including the world’s fastest, Frontier. Partnerships with major companies like Microsoft to enhance AI and cloud services, and the development of HPC6 supercomputers with Eni, underscore AMD’s strategic initiatives. Looking ahead, the revenue forecast is approximately $5.7 billion, reflecting a 6% year-over-year and 4% sequential growth. The projected non-GAAP gross margin of around 53% indicates ongoing cost efficiency improvements. However, Data Center revenue is expected to remain flat sequentially due to seasonal declines in server sales, balanced by strong GPU growth. The Client, Embedded, and Gaming segments are anticipated to face sequential declines due to seasonal factors, with a particularly significant double-digit percentage decline in semi-custom revenue. This comprehensive performance snapshot underscores the company’s strategic strengths and challenges, with robust growth in key areas countered by significant declines in others.
Industry Overview
Competition Overview
- NVIDIA is a leader in the GPU market, holding an 18% market share in 2019. Despite this dominance, AMD has been
increasing its share by offering more affordable GPUs. - Intel held a commanding 63% share of the PC GPU market in 2019. The company reported nearly $78 billion in revenue
by March 2022, but it faces rising competition from AMD and NVIDIA in both CPU and GPU markets. - Broadcom excels in semiconductors and infrastructure software. Known for consistently increasing its dividends over the past decade, Broadcom’s primary competition is not in the GPU market but in broader semiconductor fields.
Product Mix
- CPUs: AMD’s Ryzen processors cater to both desktop and laptop users, known for delivering impressive performance and
efficiency. Their EPYC processors are aimed at data centers, providing robust and scalable computing solutions. - GPUs: The Radeon series includes a range of graphics cards designed for gaming enthusiasts and professionals, offering
top-tier visual performance and advanced features. - Data Center Products: EPYC processors and Instinct accelerators are critical for data centers, supporting demanding high-
performance computing and AI tasks. - Embedded Systems: AMD’s Ryzen Embedded and EPYC Embedded processors are used in various industrial applications, valued for their reliability and power efficiency.
- Embedded Systems: AMD’s Ryzen Embedded and EPYC Embedded processors are used in various industrial applications, valued for their reliability and power efficiency.
- Software Solutions: AMD provides software like ROCm for high-performance computing and Radeon Software for gamers, enhancing overall user experience and performance.
- Gaming Consoles: AMD designs custom solutions for major gaming consoles such as PlayStation and Xbox, ensuring smooth and high-performance gaming experiences.
- Automotive Technologies: In the automotive sector, AMD offers advanced driver assistance systems and in-vehicle infotainment solutions, aimed at improving safety and user experience.
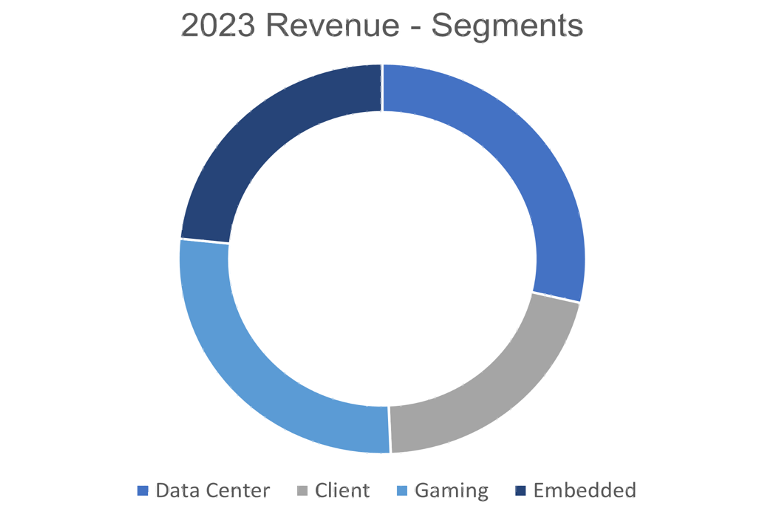
Data Center Segment
- Comprised of GPU and CPU development, 2023 Revenue = $6.5 Billion (7% annual growth) and 28.6% of total revenue.
Client Segment
- Processors designed for desktop and laptop computers, 2023 Revenue = $4.7 Billion (25% annual decline) and 20.7% of total revenue.
Gaming Segment
- Semi-custom products used in gaming consoles, alongside Radeon graphics cards, 2023 Revenue = $6.2 Billion (9% annual decline) and 27.3% of total revenue.
Embedded Segment
- Processors for embedded systems with industrial and automotive applications, 2023 Revenue = $5.3 Billion (17% annual
growth) and 23.3% of total revenue.
Introduction to AMD-Owned Brands
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) has strategically acquired several brands over the years to enhance its product portfolio and expand its market reach. These acquisitions have allowed AMD to diversify its offerings and strengthen its position in key technology sectors.
Major Brands Owned by AMD
Xilinx
Acquired in 2022, Xilinx specialises in adaptive computing and advanced Field-Programmable Gate Array (FGPA) technology. There main products are the Versal ACAP, used in data centers, 5G infrastructure, and AI acceleration. The acquisition allows AMD to enter new markets such as adaptive computing and 5G, providing a competitive edge in AI and machine learning applications.
Pensando
Acquired in 2022, Pensando focuses on distributed services platforms and innovative data processing units (DPUs). Pensando’s technology bolsters AMD’s data center solutions, providing ehanced security and performance features.
Nitero
Acquired in 2017, Nitero is known for its wireless virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) solutions. There main products consist of wireless VR technology that reduces latency and increases the immersive expereince for users. Nitero’s technology aligns with AMD’s push into the VR and AR markets, expanding its product offerings beyond traditional computing.
Revenue Contribution From Acquired Brands
Xilinx: The Xilinx acquisition significantly boosted AMD’s financial performance. In 2023, the Embedded segment, which is largely driven by Xilinx’s FPGA portfolio, generated around $1.4 billion in revenue in Q4 alone. This indicates a substantial annual contribution as this segment continued to grow throughout the year.
Pensando: While specific revenue figures for Pensando aren’t explicitly broken out, it has been integrated into AMD’s Data Center Solutions Group. This group, including contributions from both organic growth and acquisitions like Pensando, generated $1.66 billion in sales in Q4 2023, marking it as a significant part of AMD’s portfolio.
Nitero: Nitero, specializing in wireless VR technology, is a smaller part of AMD’s portfolio and its revenue contributions are not
separately listed in AMD’s financial reports. It’s likely that Nitero’s contributions are included within the broader category of AMD’s Gaming and Graphics segment, which has seen strong performance but specific revenue attributions to Nitero are not detailed.
Conclusion
AMD’s strategic acquisitions, including Xilinx, Pensando, and Nitero, have significantly bolstered its product portfolio and market reach. Xilinx has enhanced AMD’s capabilities in adaptive computing and AI, driving substantial revenue in the Embedded segment. Pensando has strengthened AMD’s data center solutions, contributing notably to the Data Center Solutions Group’s performance. Nitero’s technology aligns with AMD’s expansion into VR and AR markets. These acquisitions have not only diversified AMD’s offerings but also positioned it strongly in key technology sectors, fostering sustained financial growth and competitive advantage.
Management’s Voice
- AMD’s management expressed satisfaction with the solid performance in Q1 2024, highlighting strong results in the Data Center and Embedded segments. They emphasized the successful launch of new Ryzen processors and Radeon GPUs, which contributed to overall growth despite a challenging market environment.
- Looking ahead, AMD is optimistic about continued growth driven by demand for data center and AI solutions. Management aims to capitalize on their product innovations and strategic partnerships to expand market share. They are also focused on improving operational efficiency and cost management to enhance profitability.
Investment Risks
Technological Changes
Rapid advancements in technology necessitate significant investments in research and development (R&D). AMD must continuously innovate to keep pace with these changes or risk its products becoming obsolete. The company mitigates this risk by heavily investing in R&D to remain at the forefront of technological advancements in GPUs and CPUs, ensuring that it can deliver cutting-edge solutions to the market.
Supply
AMD relies on third-party manufacturers like TSMC for semiconductor fabrication, making it vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. Any interruption in the supply chain can delay product releases and negatively impact revenue. To address this risk, AMD diversifies its supplier base and invests in robust supply chain management practices to ensure continuity
and reliability in its operations.
Economic and Geopolitical Factors
Global economic conditions and geopolitical tensions can significantly impact AMD’s operations. Trade restrictions, tariffs, and political instability can disrupt supply chains and market access. AMD mitigates these risks by maintaining a global presence and strategically managing its operations to navigate regional challenges effectively.
Intellectual Property Risks
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on intellectual property (IP), and AMD must protect its IP to maintain its competitive edge. Global economic conditions and geopolitical tensions can significantly impact AMD’s operations. Infringement claims or failure to protect IP could lead to costly legal battles and financial losses. AMD addresses this risk by focusing on patent protection and maintaining legal vigilance to defend against IP infringement.
Regulatory Compliance
AMD operates in a highly regulated industry, subject to various laws and regulations globally. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in fines, legal actions, and operational disruptions. The company continuously monitors regulatory changes and ensures compliance across all its operations to mitigate this risk.
Conclusion
AMD faces several investment risks including rapid technological changes, supply chain disruptions, economic and geopolitical
factors, intellectual property risks, and regulatory compliance. The company mitigates these risks through significant R&D
investments, diversifying its supplier base, maintaining a global presence, and focusing on patent protection and legal vigilance. By continuously monitoring and adhering to regulatory changes, AMD ensures compliance across its operations, thereby maintaining its competitive edge and ensuring business continuity in a highly dynamic industry.
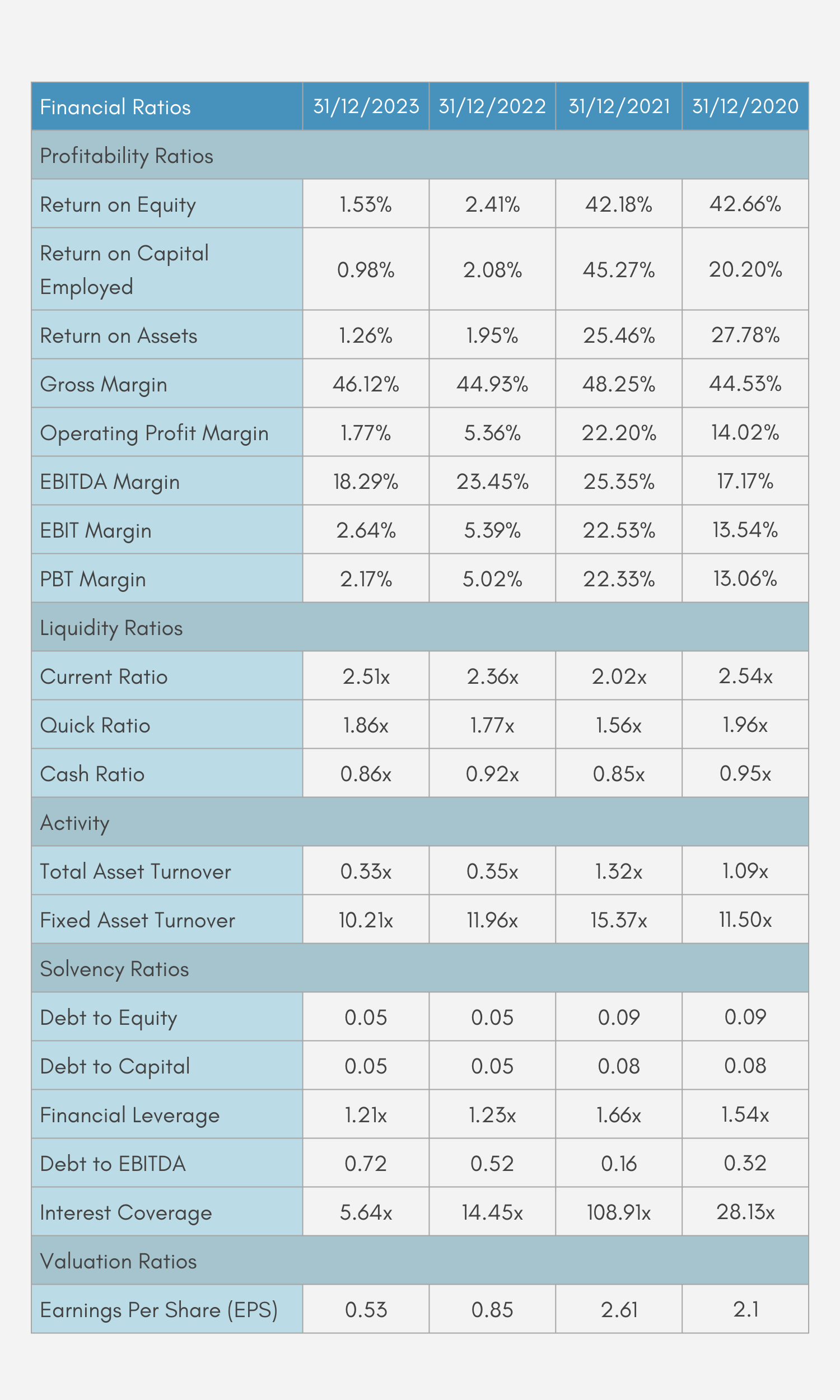
Detailed Ratio Analysis
Conclusion
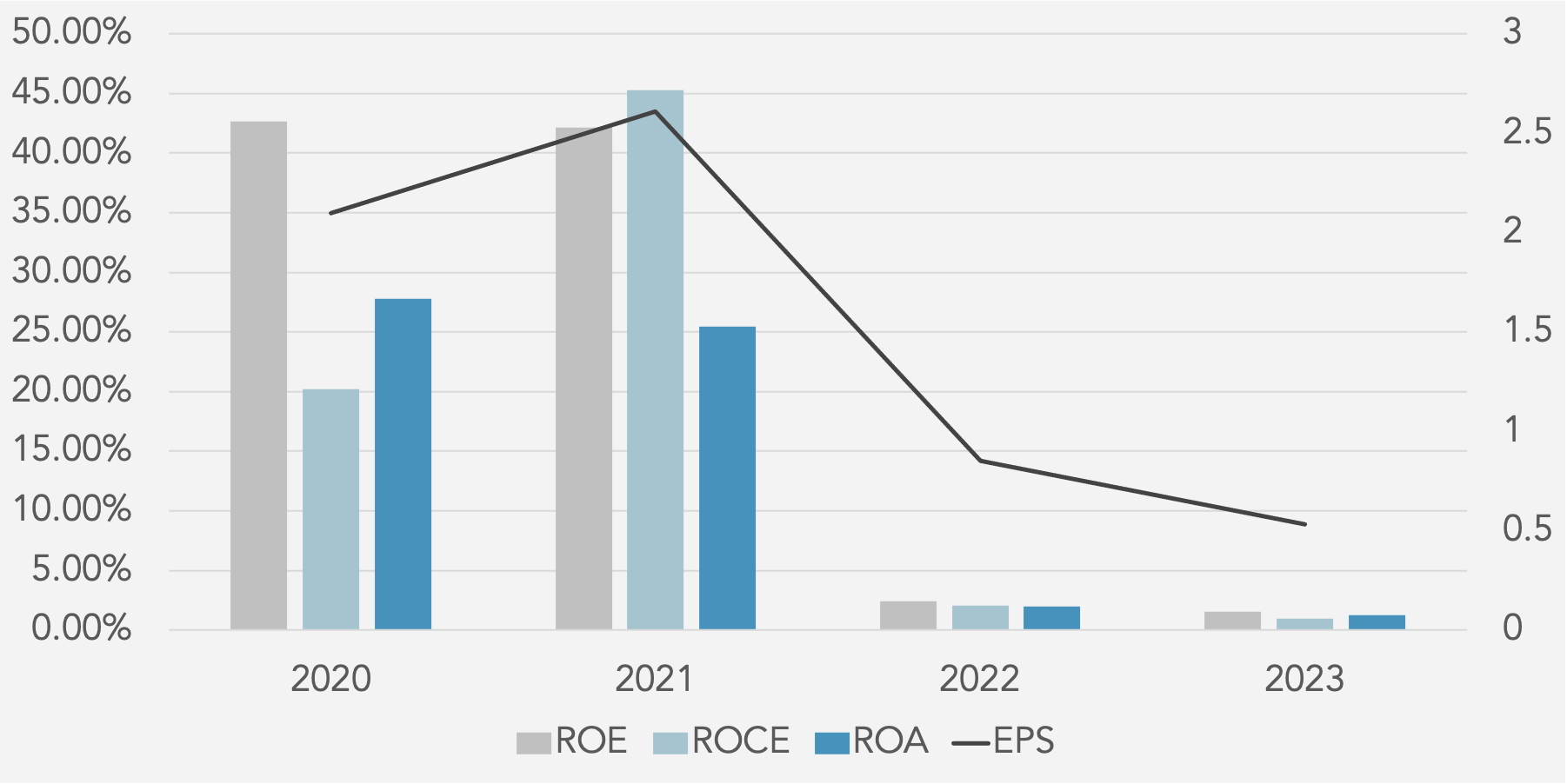
The financial ratios from 2020 to 2023 reveal several concerning trends for the company. The most striking negative trend is the
significant decline in profitability metrics. Return on Equity (ROE) has plummeted from 42.66% in 2020 to just 1.53% in 2023,
indicating a drastic reduction in the company’s ability to generate profit from shareholders’ equity. Similarly, Return on Capital
Employed (ROCE) has fallen from 45.27% in 2021 to a mere 0.98% in 2023, suggesting a severe drop in the efficiency of capital
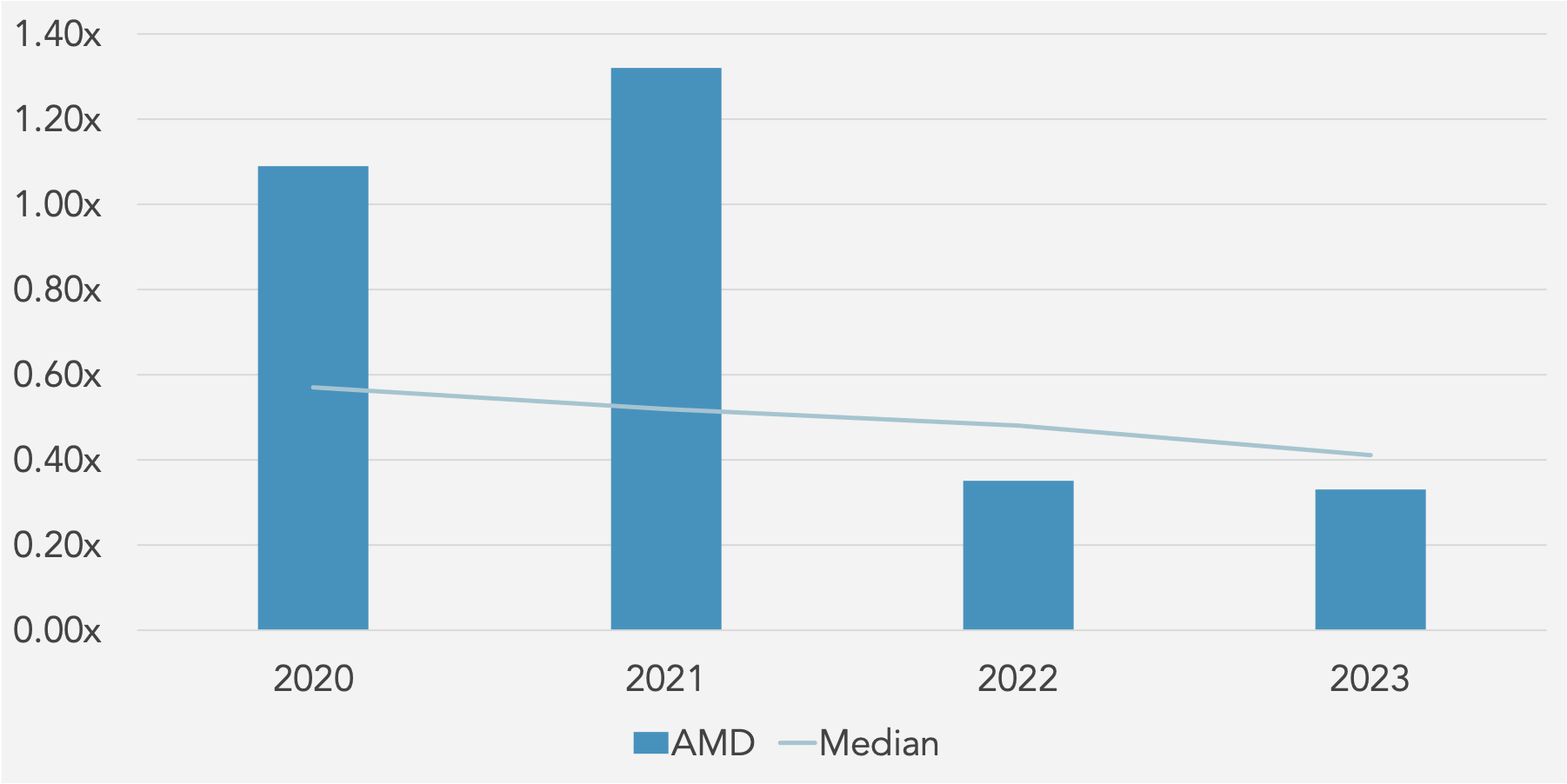
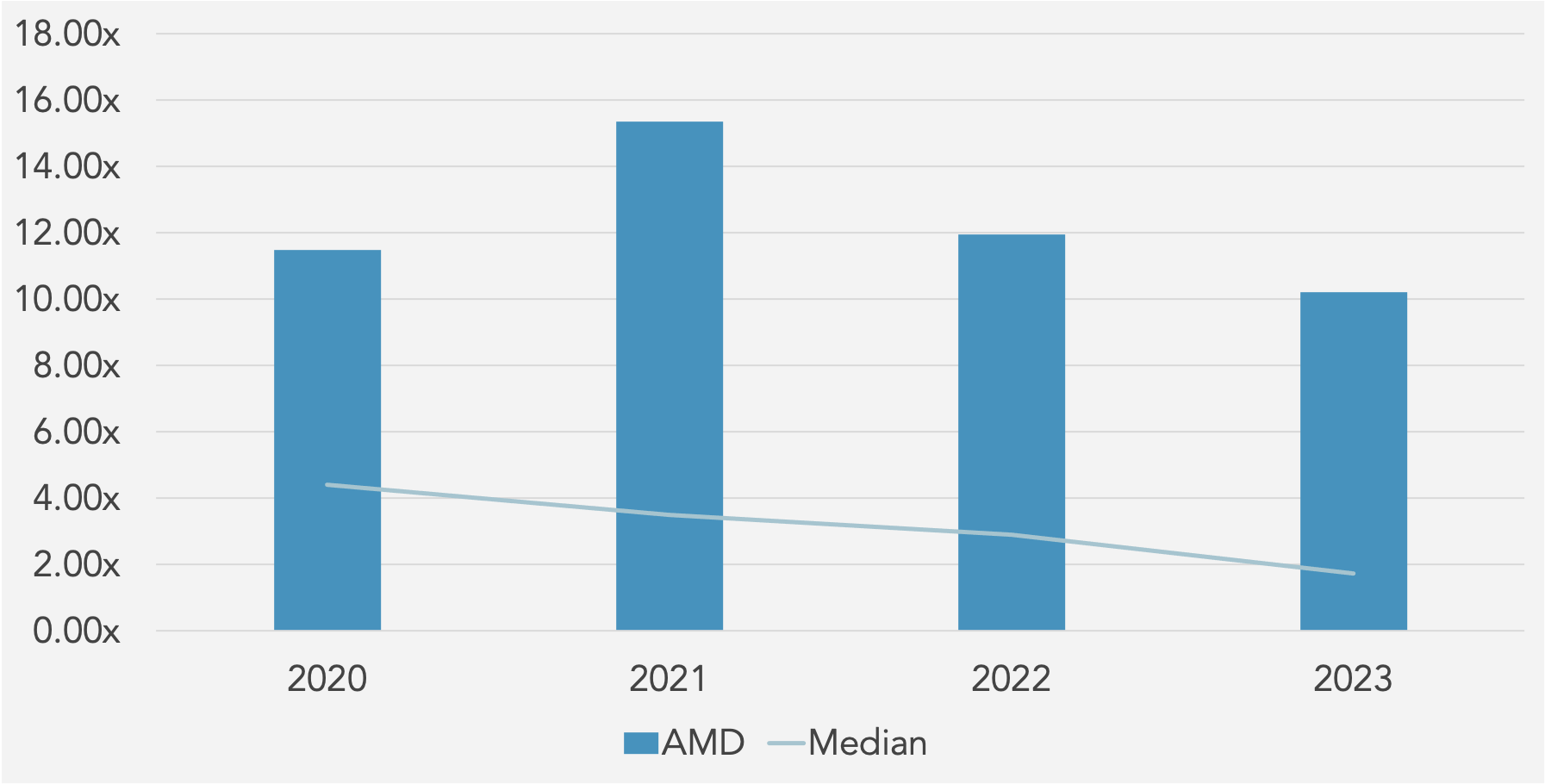
utilization. Return on Assets (ROA) has also seen a sharp decrease from 27.78% in 2020 to 1.26% in 2023, highlighting a decline in asset efficiency. Operating Profit Margin has reduced significantly from 22.20% in 2021 to 1.77% in 2023, indicating that operational efficiency has diminished considerably. EBITDA Margin and EBIT Margin have both declined, with EBITDA Margin falling from 25.35% in 2021 to 18.29% in 2023, and EBIT Margin dropping from 22.53% to 2.64% over the same period. The PBT Margin has similarly decreased from 22.33% in 2021 to 2.17% in 2023. On the liquidity front, while the Current Ratio and Quick Ratio have improved slightly, indicating better short-term financial stability, the Cash Ratio has declined. The Activity Ratios show a troubling decrease in Total Asset Turnover from 1.32x in 2021 to 0.33x in 2023, and Fixed Asset Turnover has also declined. In terms of solvency, the Debt to Equity and Debt to Capital ratios have remained stable but low, while Financial Leverage has decreased from 1.66x in 2021 to 1.21x in 2023, which could be seen as a positive reduction in reliance on debt. However, the Interest Coverage ratio has dropped dramatically from 108.91x in 2021 to 5.64x in 2023, raising concerns about the company’s ability to cover interest expenses. Lastly, Earnings Per Share (EPS) has fallen significantly from 2.61 in 2021 to 0.53 in 2023, indicating a substantial decrease in profitability per share. These trends suggest that while there are some improvements in liquidity, the overall financial health of the company has deteriorated, with significant declines in profitability, asset efficiency, and interest coverage capabilities.
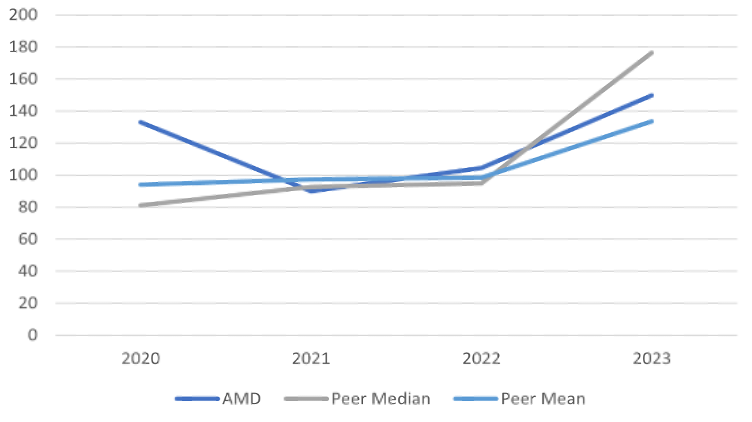
Share Price Performance
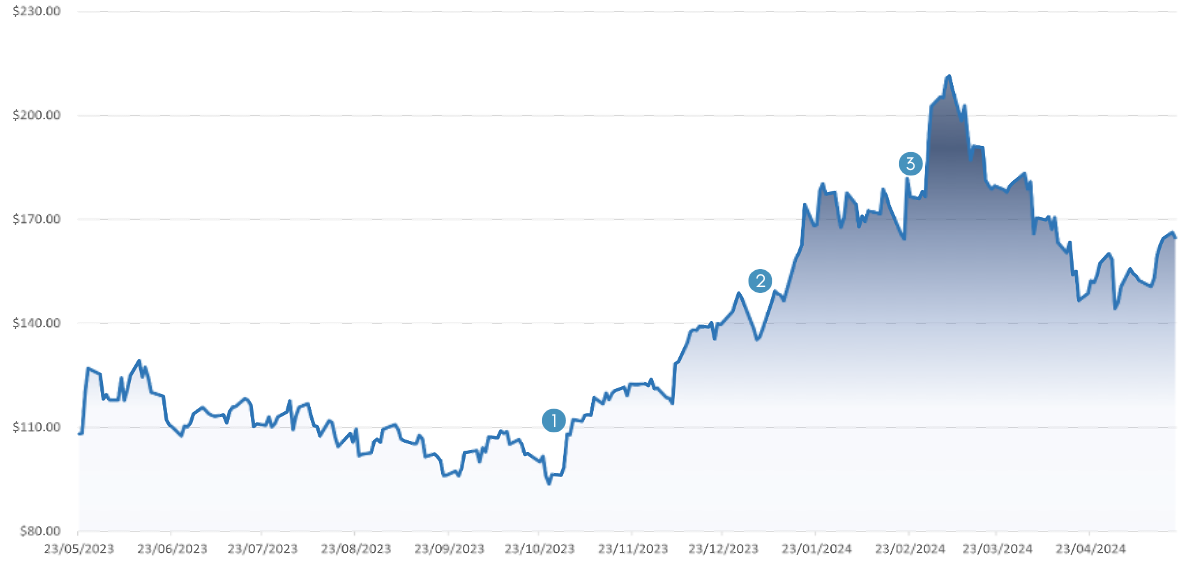
Major Events
[1]: 14th November 2023, AMD announced advancements in AI, including new AI products/partnerships. This annoucnements likely boosted investor confidence in AMD’s future growth prospects, resulting in a sharp rise in the price.
[2]: 19th January 2024, AMD reported strong fourth-quarter earnings, surpassing market expectations. High revenue growth, improved profit margins, and optimistic future guidance would have contributed to incresed investor confidence and a subsequent rise in the stock price.
[3]: 29th February 2024, AMD launched the Ryzen 8000G Series, marking a signifciant improvement in performance and AI
capabilties. This launch introduced the first desktop processors with a dedicated nerual provessing unit, enhancing AI processing
capabilities. The intial market reaction was a very positive up, however volatility followed as the market adjusted to the real-world
implications of the product launch.
Key Statistics
- IPO: Monday, 15th October 1979
- Ticker: AMD
- Market Capitalisation: $267.53 Billion
- 52wk Range: $93.11 – $227.30
Conclusion
AMD’s share price experienced substantial growth from mid-2023 to early 2024, rising from around $100 to over $200 before
stabilizing around $170. This upward trend reflects strong market confidence, likely driven by significant revenue growth, strategic acquisitions, and successful product launches. However, the subsequent decline and stabilization suggest market corrections possibly due to broader economic factors or internal financial challenges. Overall, the share price performance indicates investor optimism tempered by market realities and competitive pressures.
Financial Analysis
Revenue Development (Thousands USD)
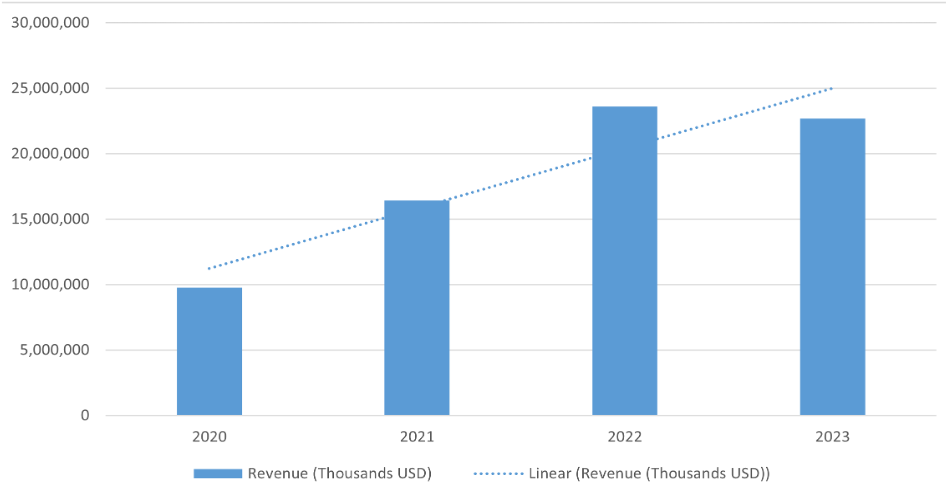
Revenue had decreased by $921,000,000 from 2022 to 2023 which is a percentage decrease of 3.90%, however revenue showed a consistent upward trend from 2020 to 2022. This growth indicates a strong period of expansion and market demand for AMD’s products. Despite the decrease in 2023, the linear trendline shows an upward slope, indicating an overall growth trajectory over the four year period.
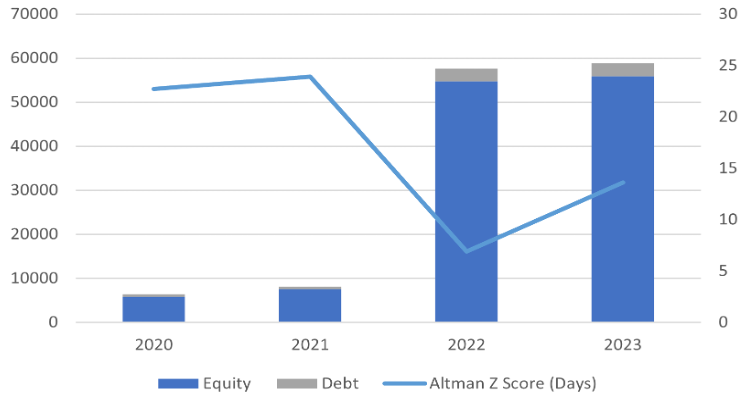
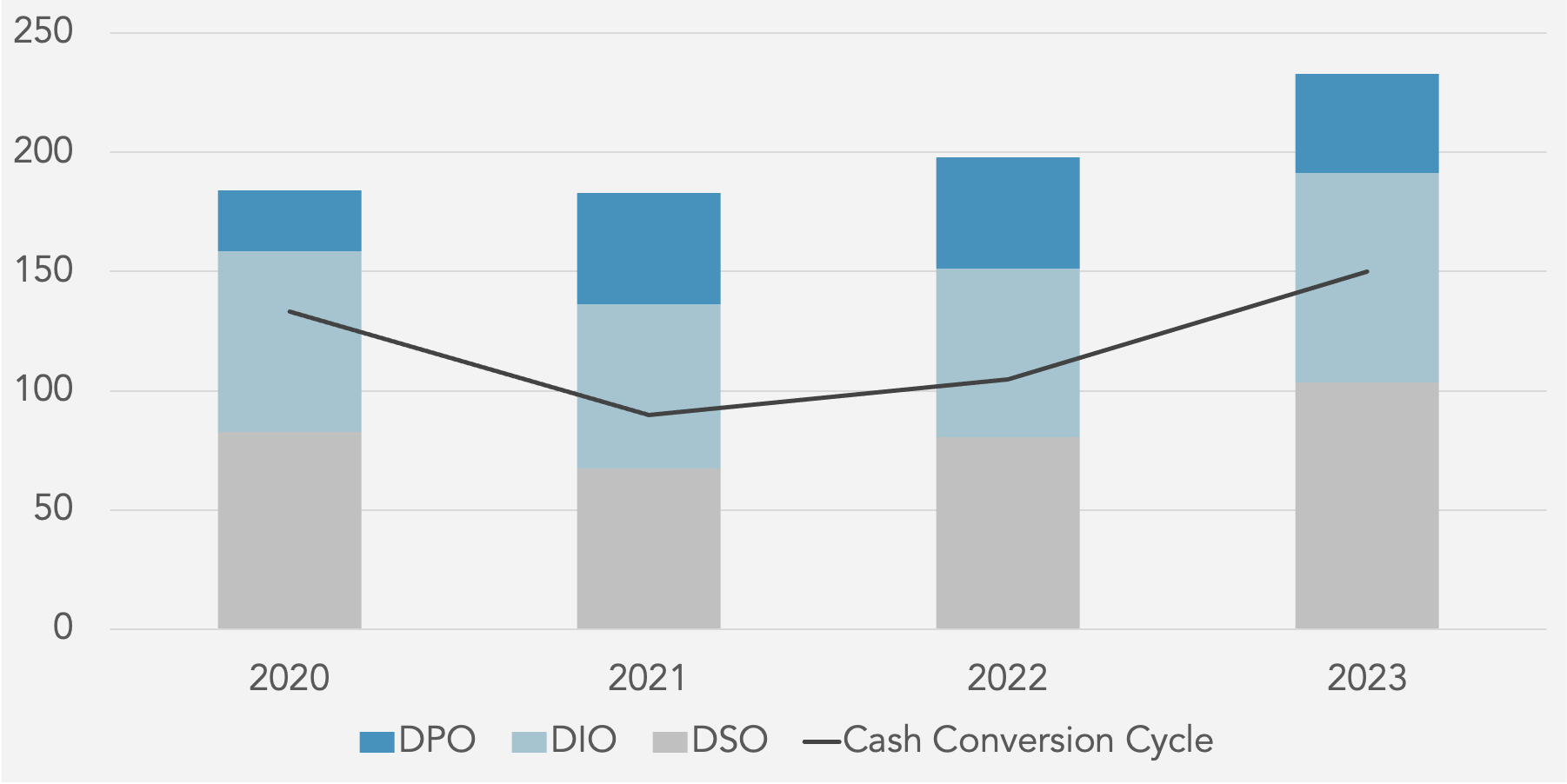
Cash Conversion Cycle Days
Equity, Debt and Altman-Z Score (Millions USD)
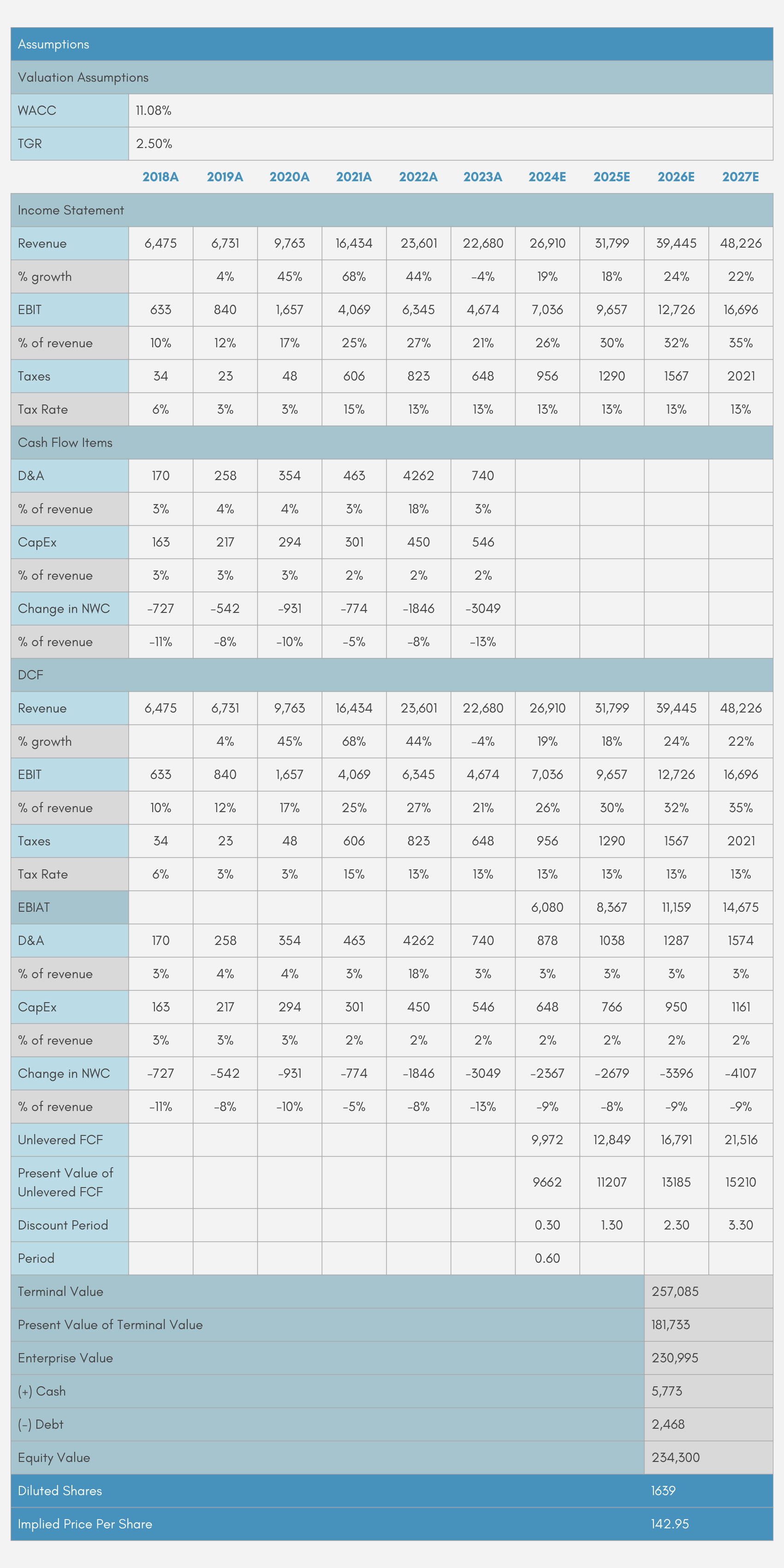
Valuation (DCF)
P&L Statement Growth (Millions USD)
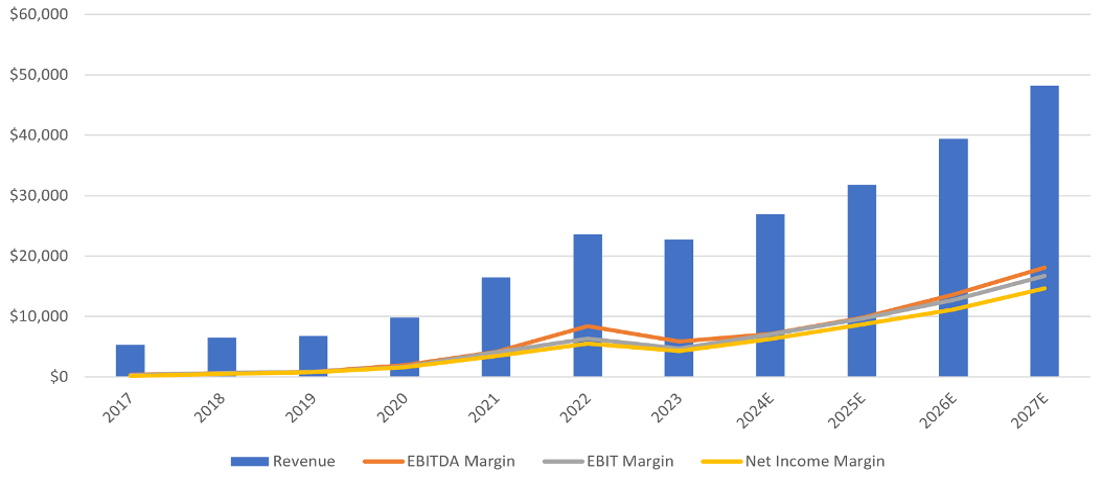
Target Price
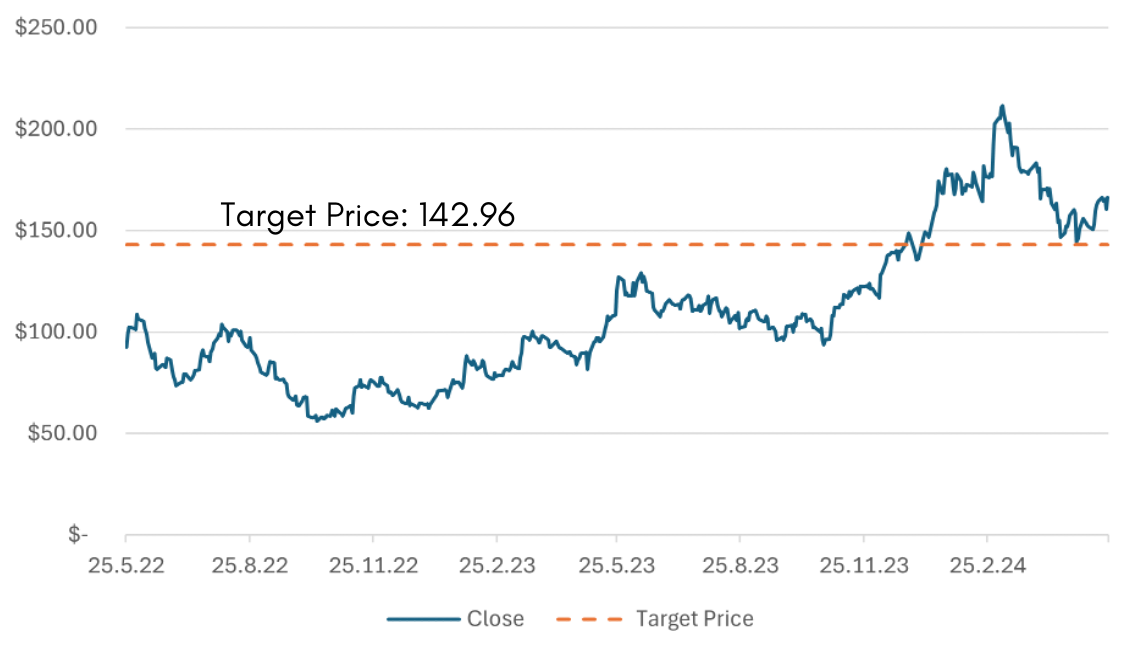
Target: $142.95
Downside Potential of -14.1%
Currently $166.36
Appendix – Financial Analysis
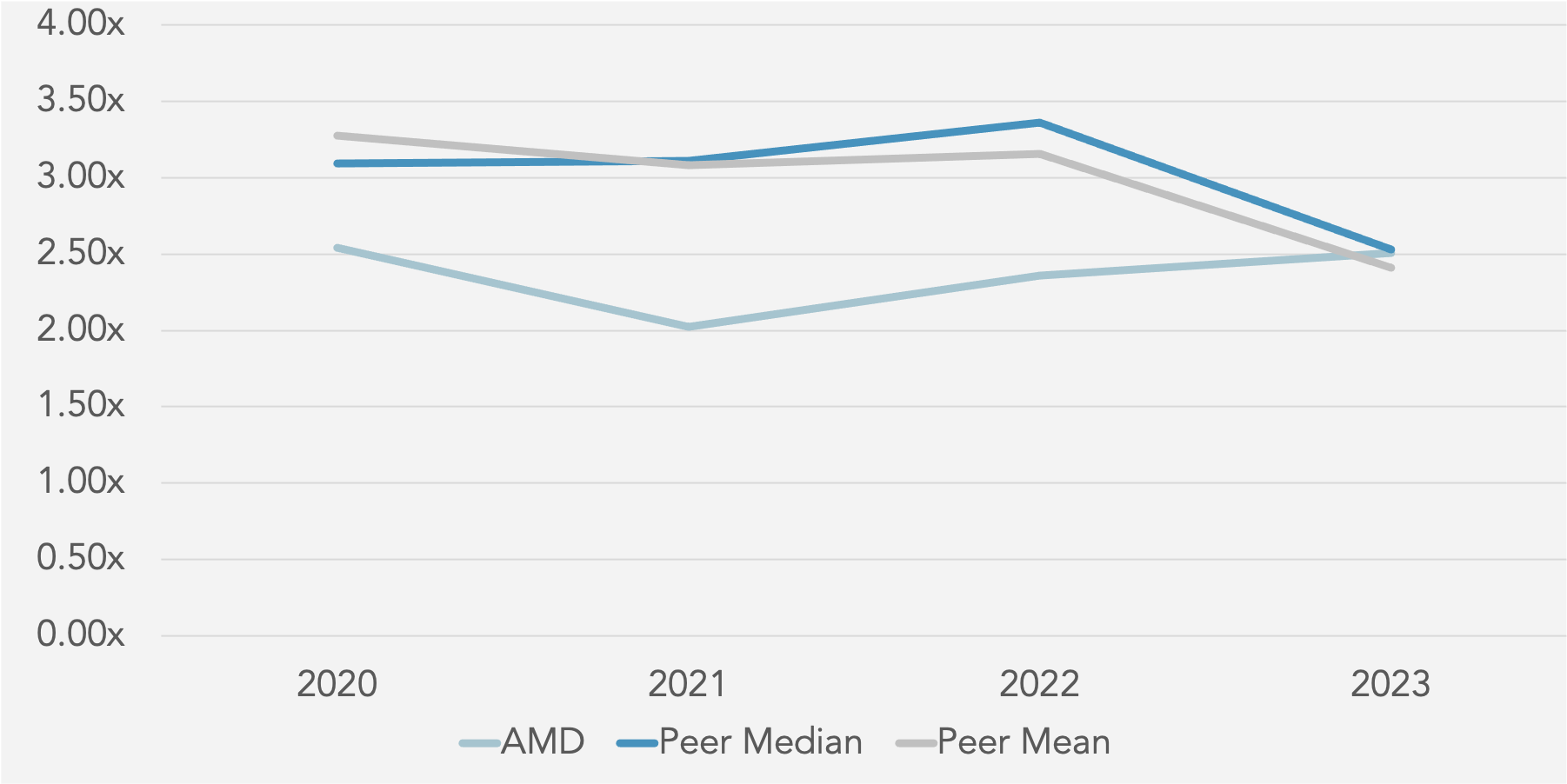
Asset Utilisation
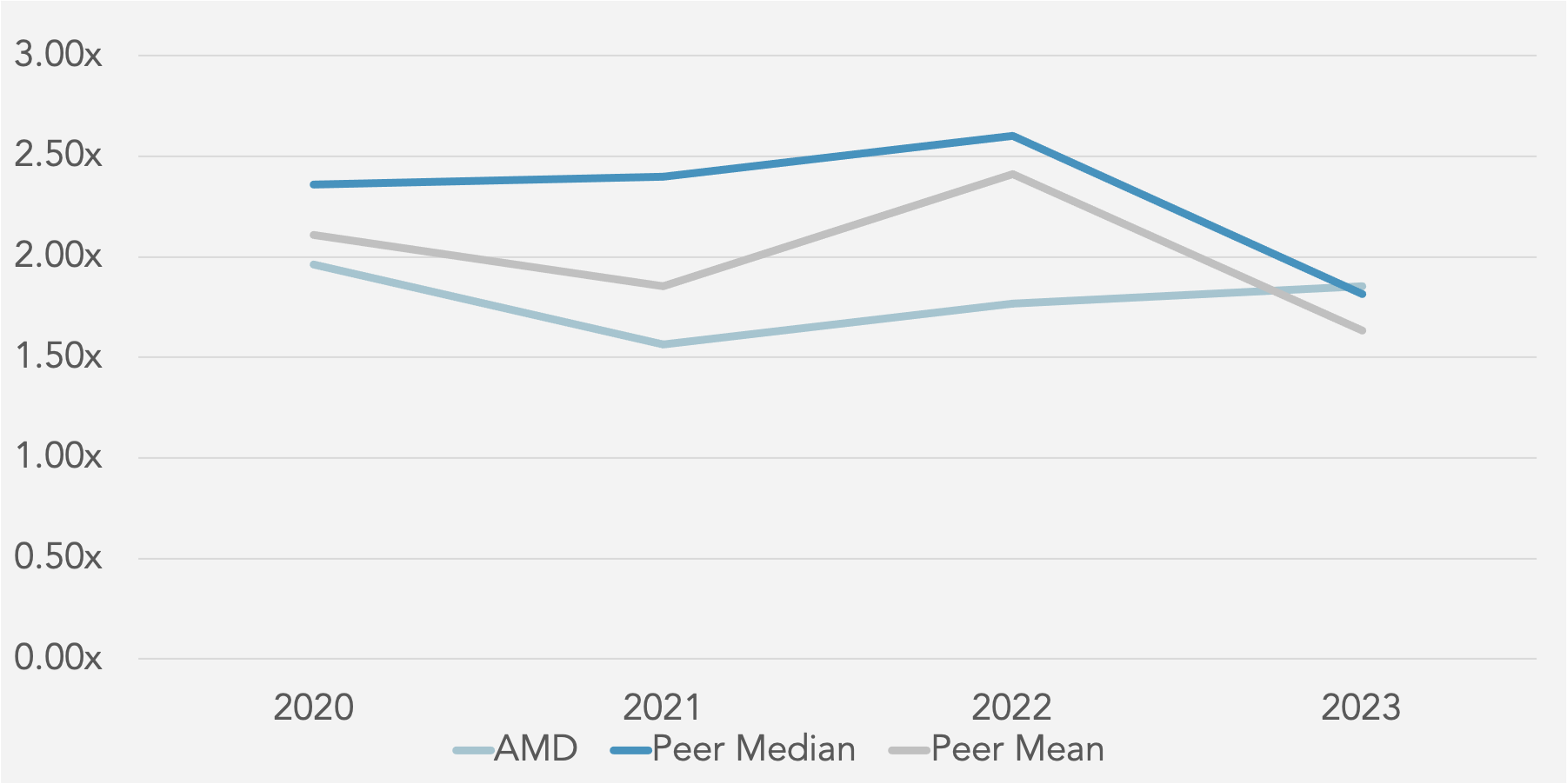
Total Asset Turnover (x) against Peer Median
Fixed Asset Turnover (x) against Peer Median
Margin Analysis
Gross Profit Margin (%) against Peer Median
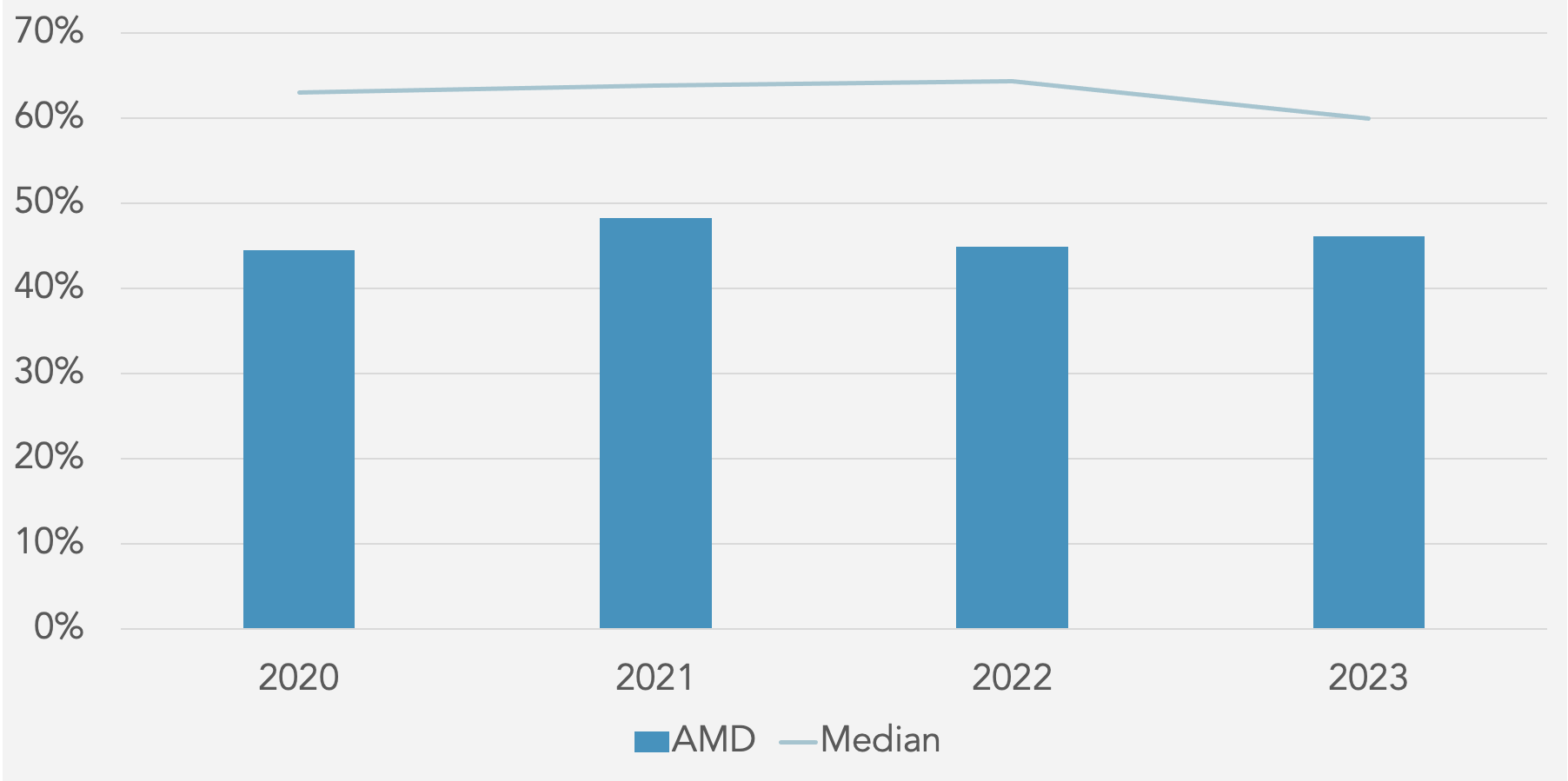
Operating Profit Margin (%) against Peer Median
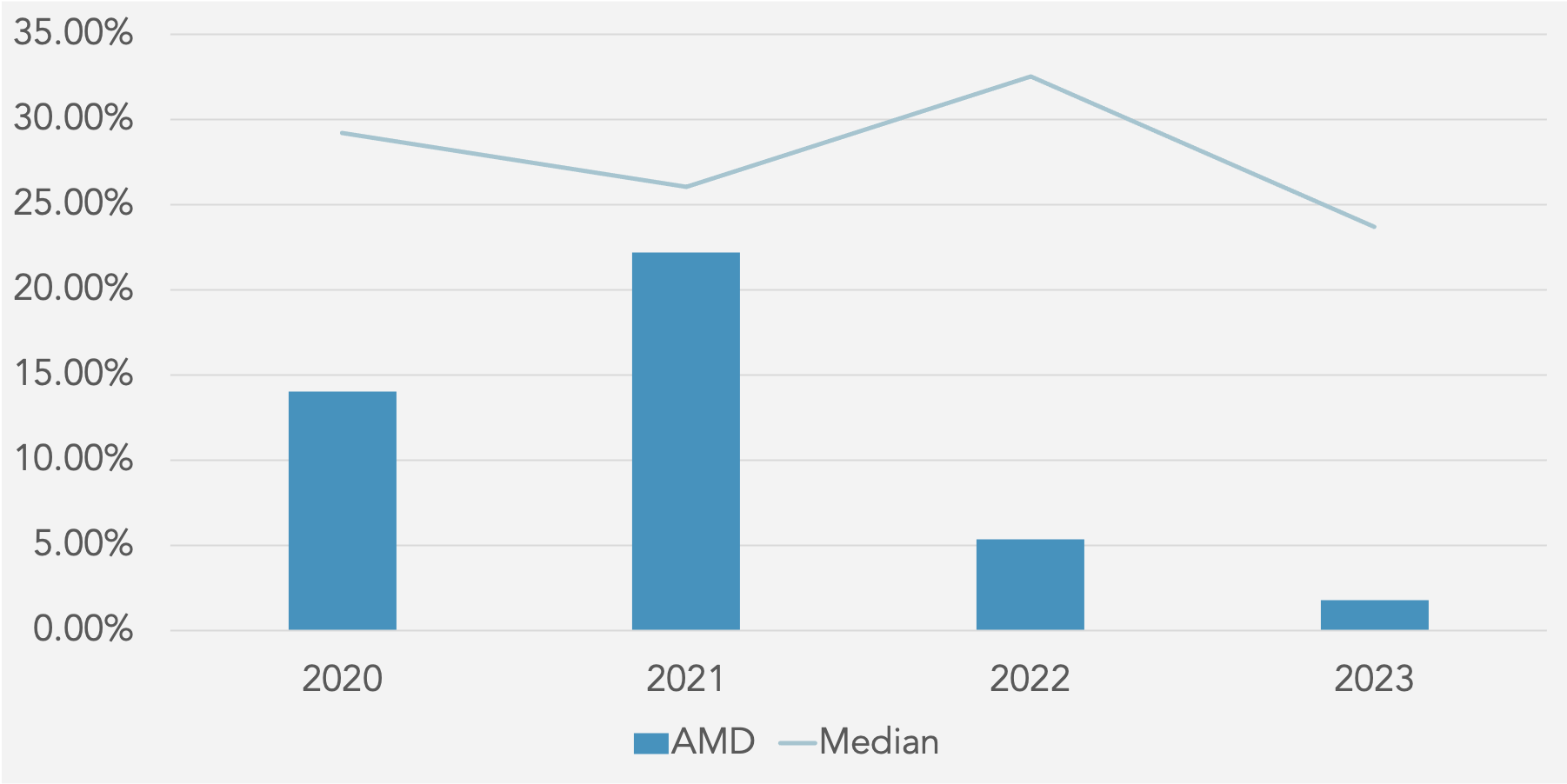
Net Income Margin (%) against Peer Median
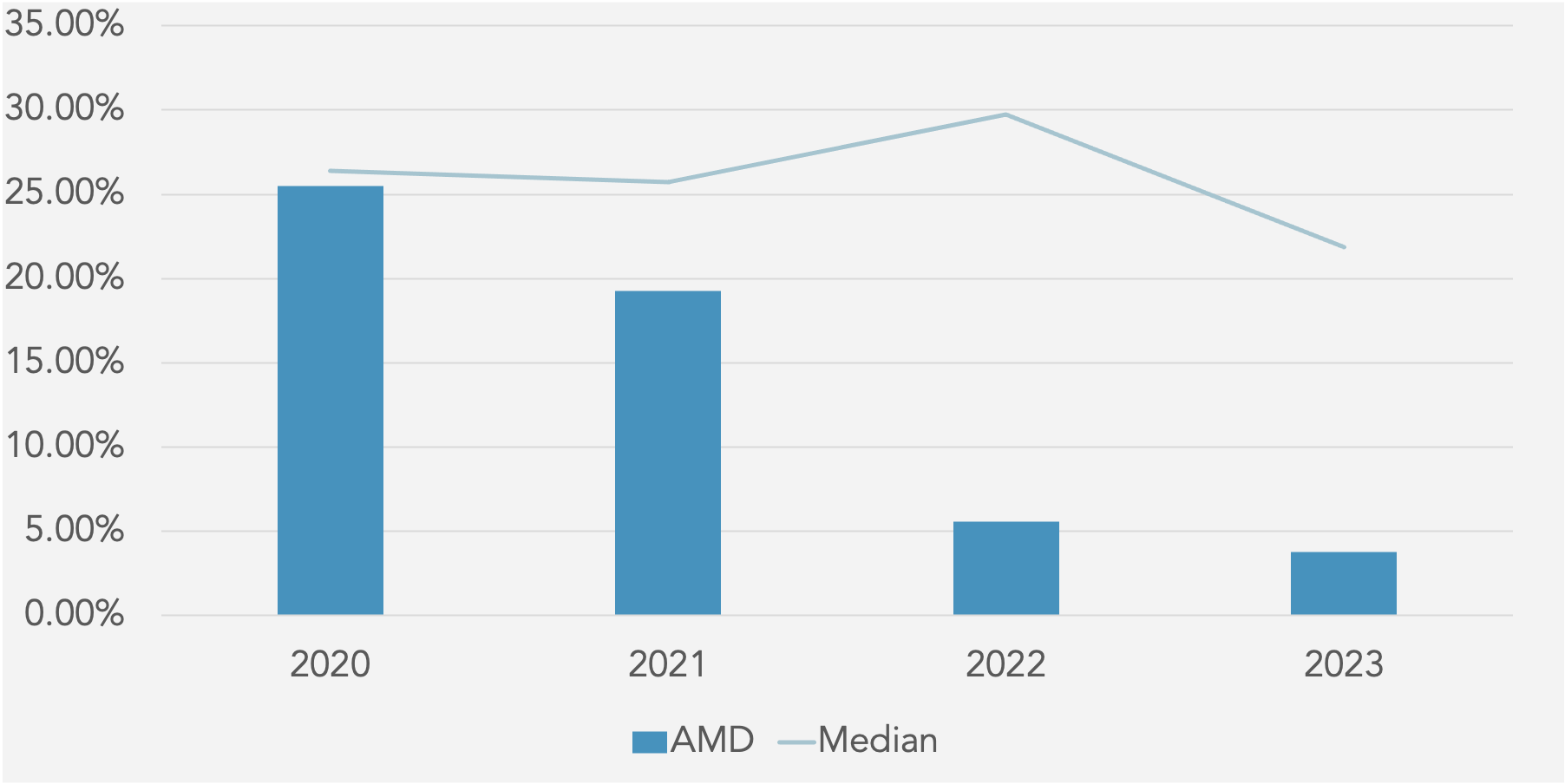
Working Capital Analysis
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) against Peer Median
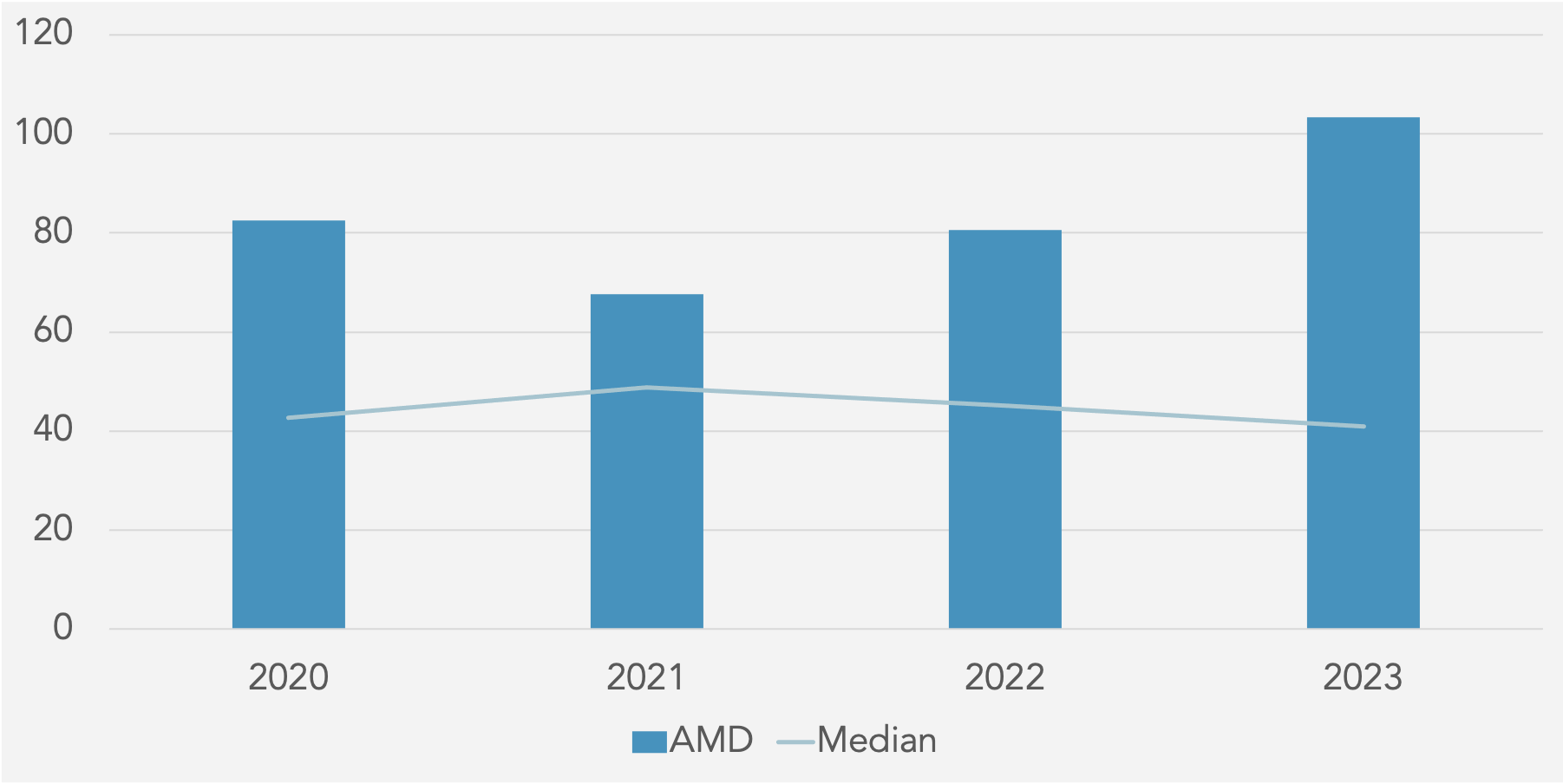
Days Inventory On-Hand (DIO) against Peer Median
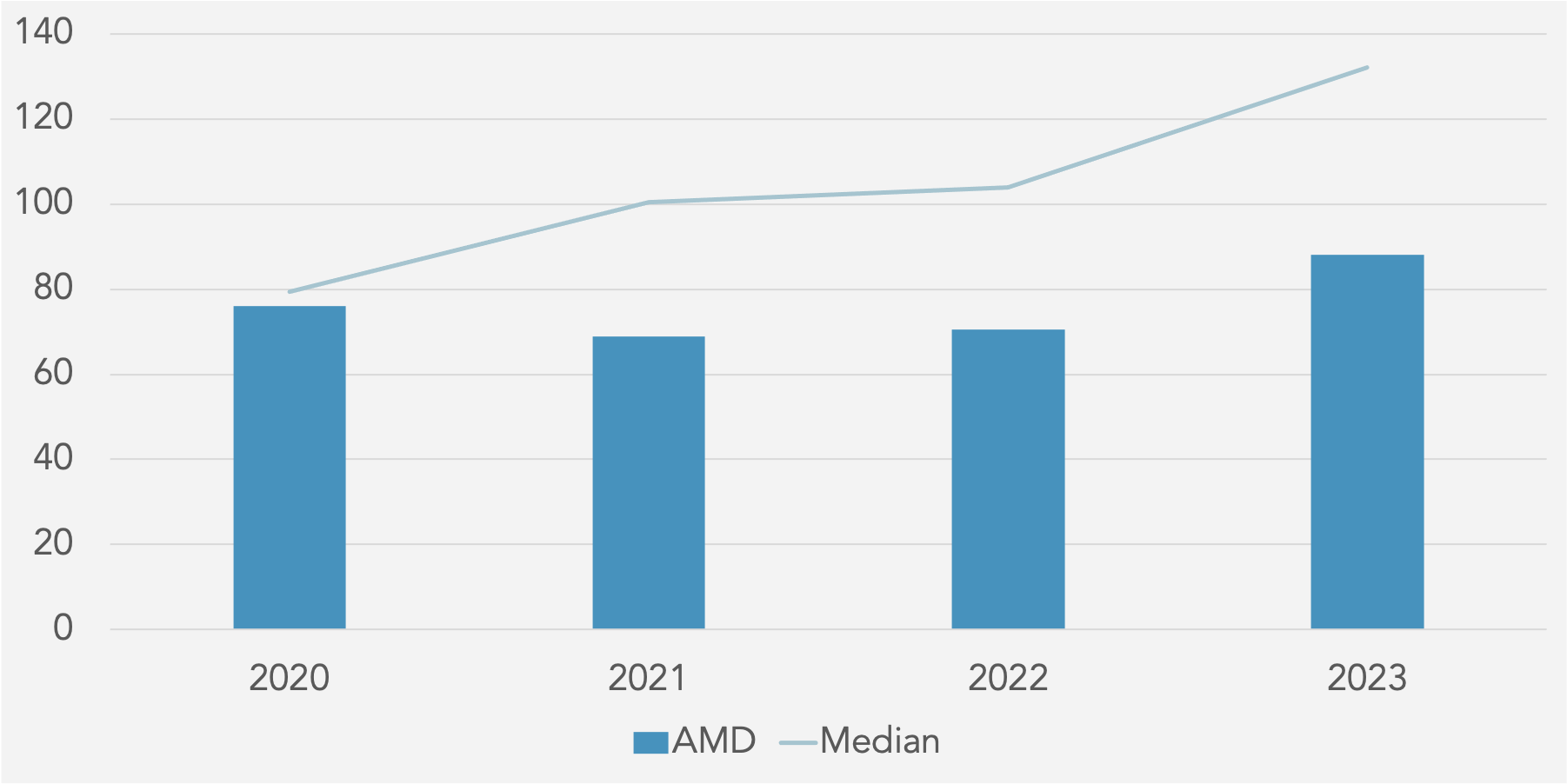
Days Payables Outstanding (DPO) against Peer Median
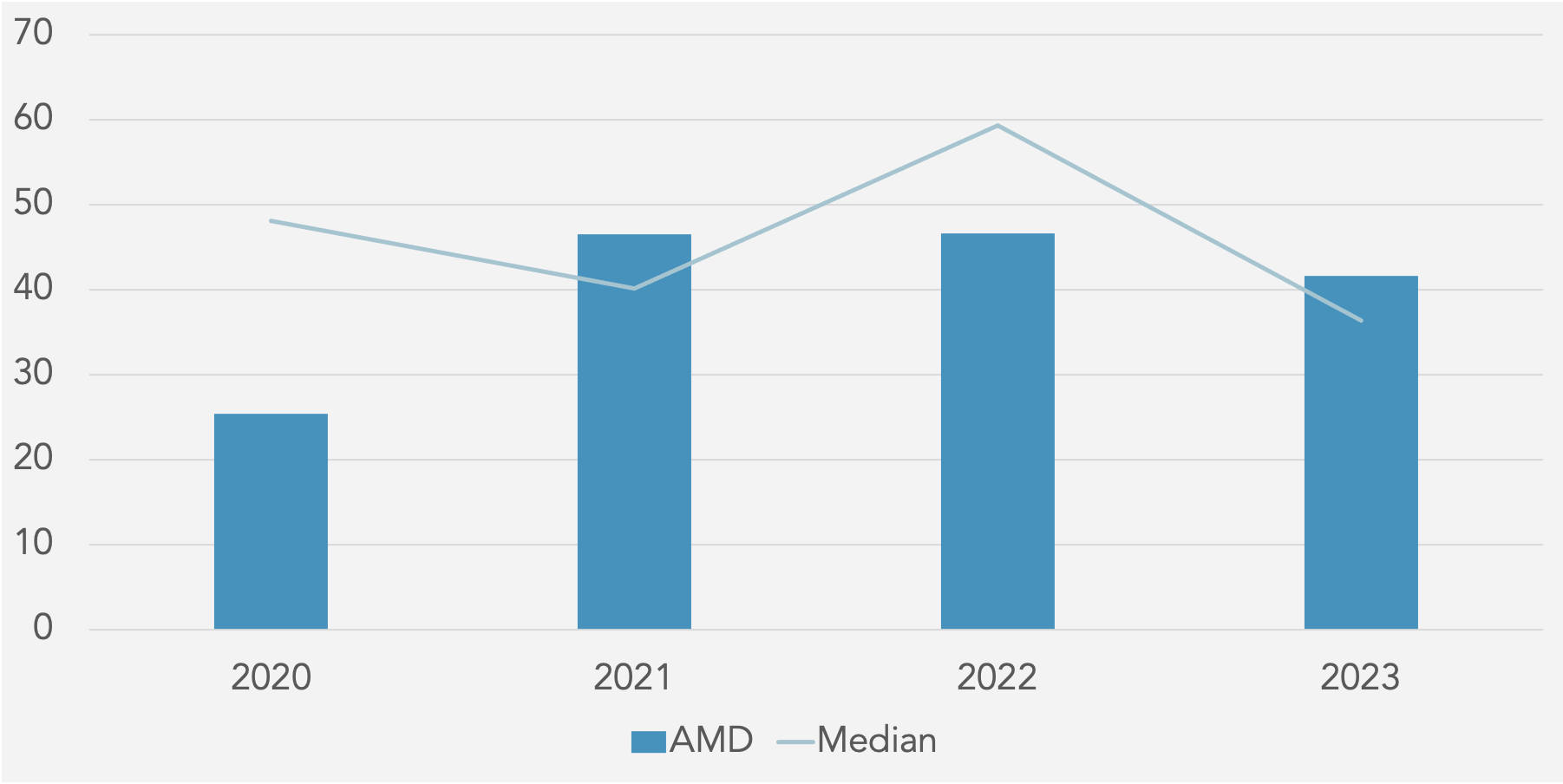
Profitability Metrics
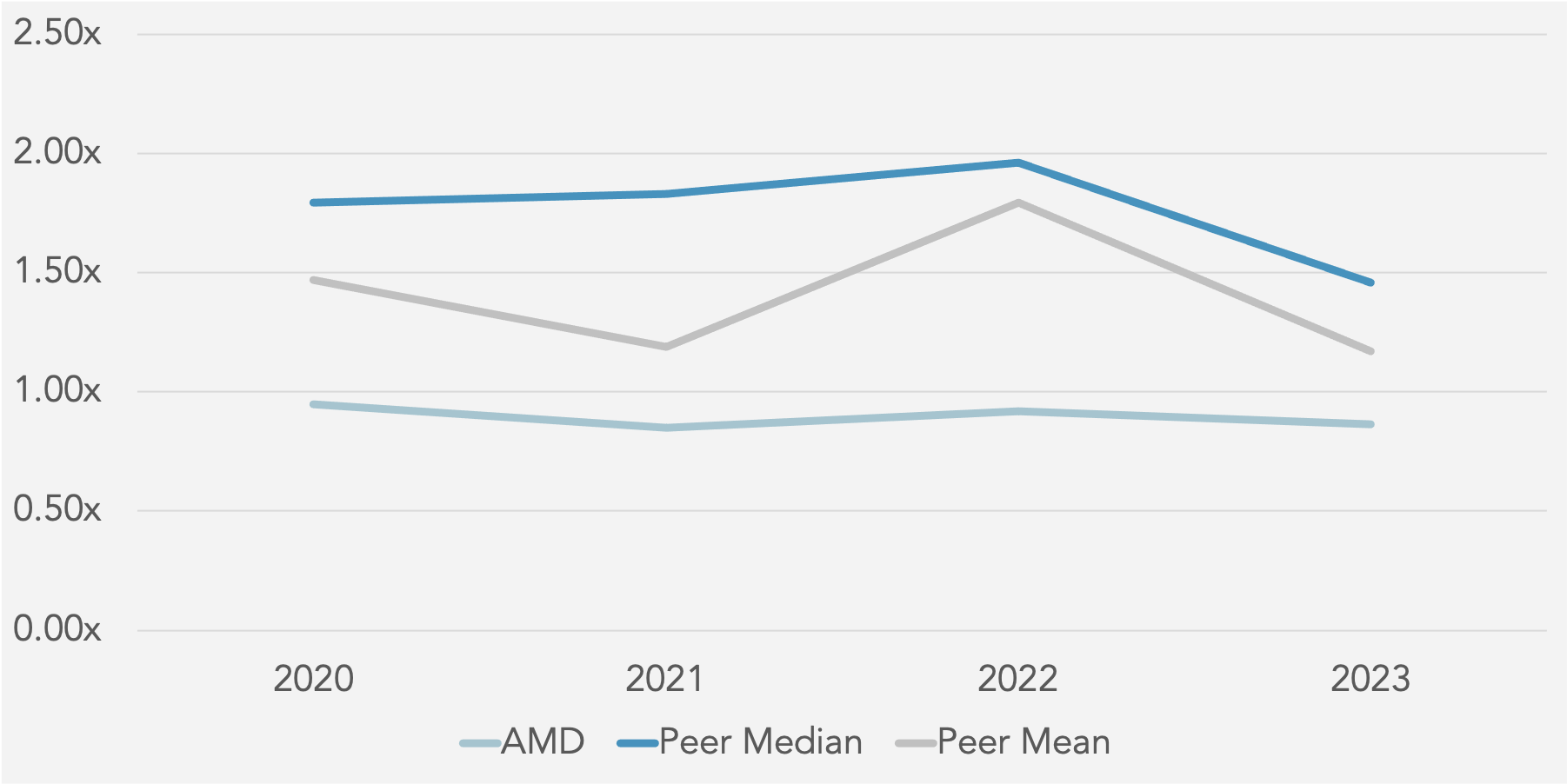
Return on Equity (%) against Peer Median
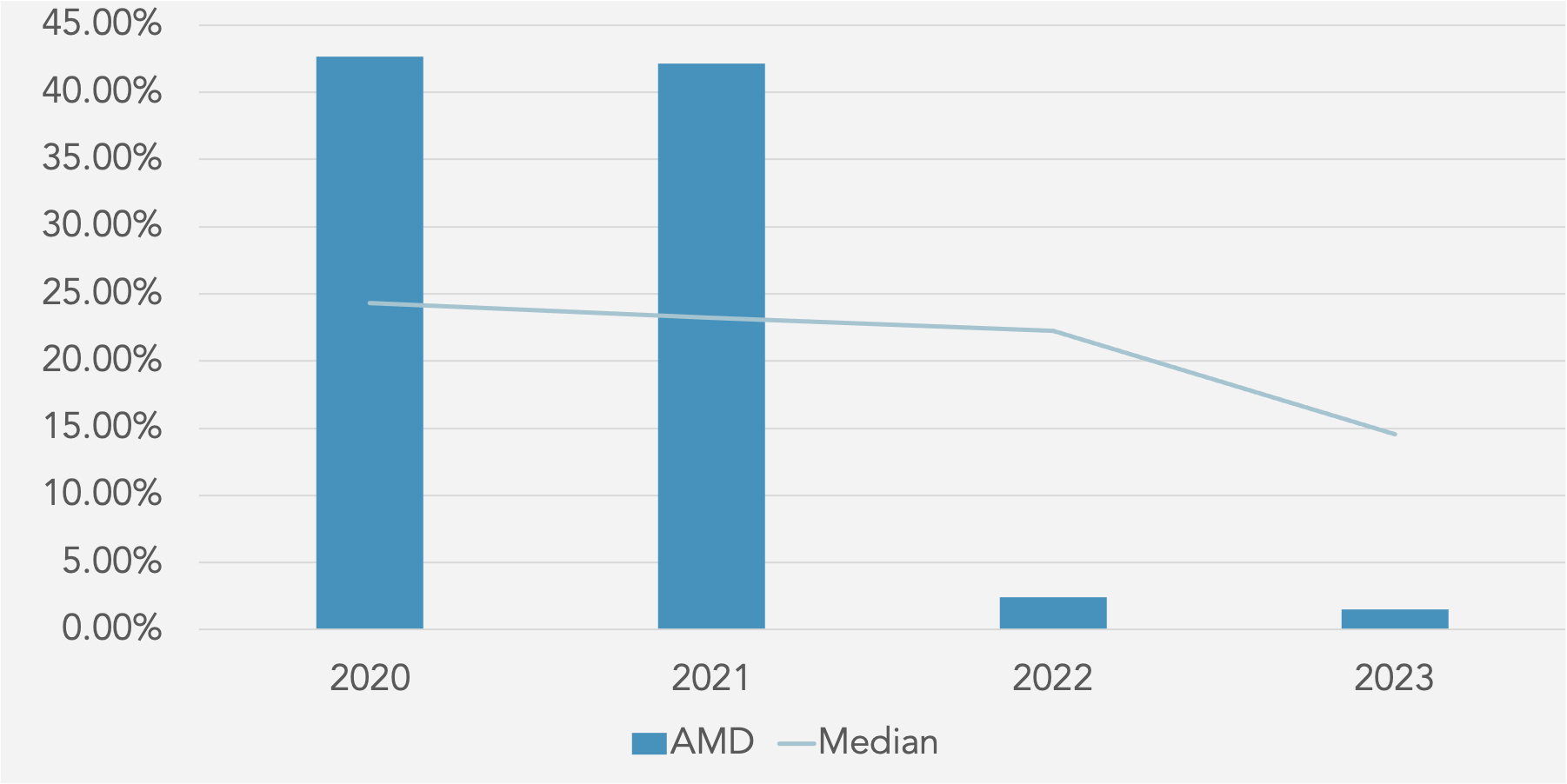
Return on Assets (%) against Peer Median
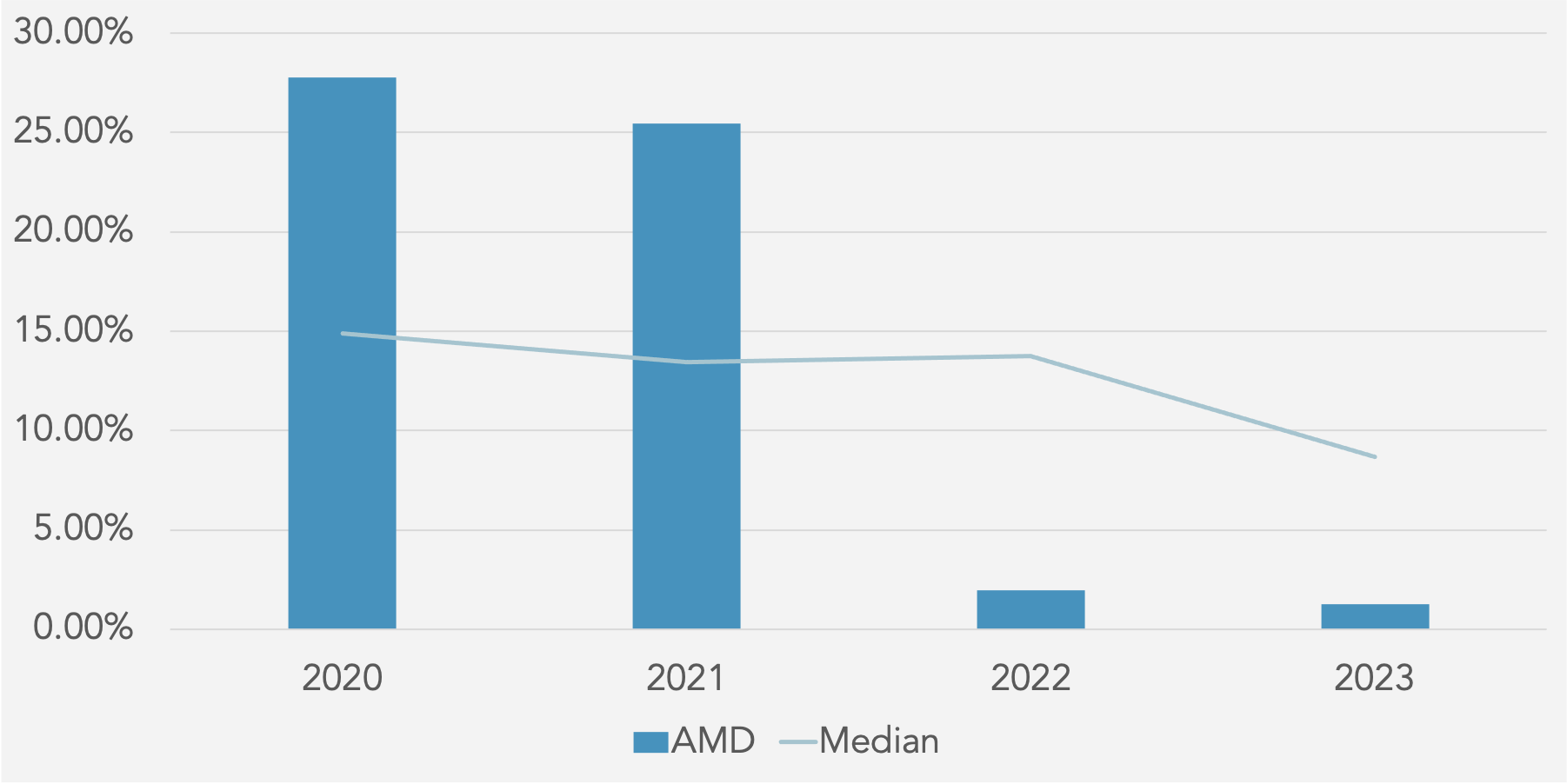
Liquidity and Solvency
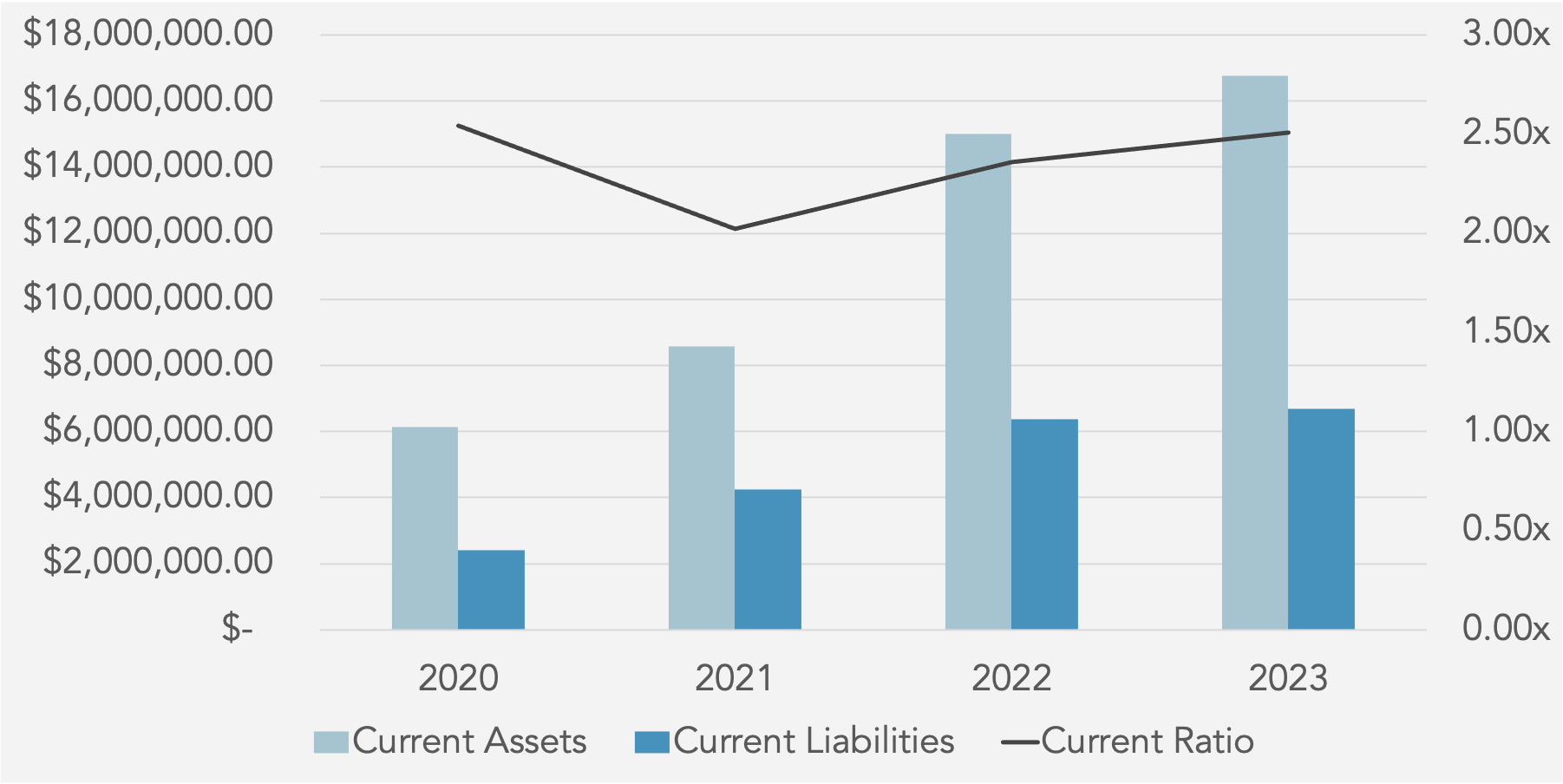
Current Ratio
Quick Ratio
Cash Ratio
Profitability, working capital and liquidity
Profitability Ratios
Current Ratio (Thousands)
Working Capital Schedule (Days)
Appendix – Valuation
DCF
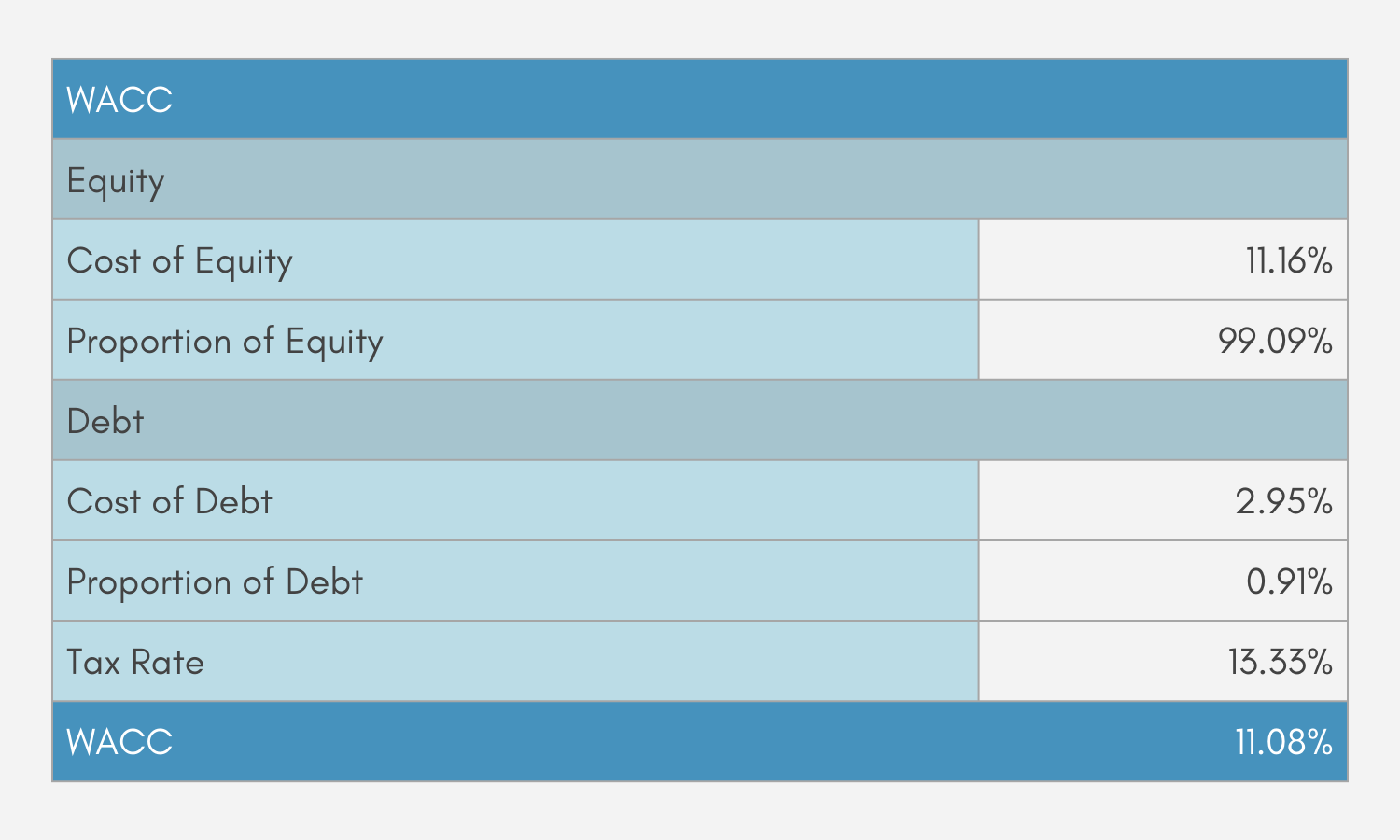
WACC Output
Appendix – SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Diverse Product Portfolio: AMD’s range of CPUs, GPUs, and APUs allows for diversified earnings across consumer and enterprise markets.
Partnerships: Strong partnerships with companies like Microsoft, Sony, and Google provide stable demand.
Competitive Pricing: AMD’s competitive pricing for its Ryzen and EPYC processors has driven significant market share gains.
Weaknesses
Competitive Industry: Larger competitors like NVIDIA and Intel have more resources for marketing, distribution, and manufacturing.
Revenue Dependency: Significant revenue reliance on key segments like data centers and gaming processors.
Thinner Profit Margins: Competitive pricing leads to thinner profit margins and lower R&D spending compared to competitors.
Opportunities
Mobile Processor Market: Growing presence in the fast-growing mobile CPU market since 2021.
Data Center Growth: Increasing demand for cloud services presents an opportunity for growth in server processors due to their quality and competitive pricing.
Threats
Intellectual Property Disputes: Risk of litigation from constant innovation could lead to financial strain.
Supply Chain Dependency: Heavy reliance on external suppliers, especially from Asia, exposes AMD to potential supply disruptions.
Appendix – Profit Margin Analysis
Greater investment in research and development has led to a decline in net profit by over 20 percentage points from 2020 to 2023. This expenditure reflects the increasingly crowded market space, with the rise of TSMC and Nvidia, whose market cap is nearing $3 trillion. Therefore, steady gross and falling net and operating profit margins indicate AMD’s strategy to expand its product line. In particular, investment in AI and APU technology accounts for much of the expense.
The strategic acquisition of Xilinx in 2022 represents a diversification of AMD’s product line and R&D opportunities, particularly in adaptive computing capabilities. Acquisition-related costs have therefore eroded net profit margins. While such costs have impacted short-term profitability, the integration of new technologies and the expansion of AMD’s product line will improve the product range in the long term.
With a 5 year EBITDA CAGR of 45.7%, AMD is in the process of scaling operations and capacity, and so short term decline in margins is to be expected. A continued programme of heavy investment in future growth products thus reflects how strategic expenditures have decreased net profit margins, with the objective of fuelling sustained and rapid growth in the longer term. Therefore, whilst market conditions and competition have exerted pressure on AMD, the company remains a leader in R&D, with the prospect of innovative synergies and a widened product line.
Appendix – PESTLE Analysis
Political Factors
Trade Policies and Tariffs: AMD is affected by international trade policies and tariffs, especially between the U.S. and China, as it has significant operations and markets in both countries. For instance, the fluctuation of tariffs on Chinese- manufactured components due to ongoing geopolitical tensions has necessitated adjustments in AMD’s sourcing strategies.
Economical Factors
Global Economic Conditions: During economic downturns, as seen in the 2008 Financial Crisis, or during the COVID-19 Pandemic, consumer and business spending on technology products can decline sharply. Conversely, economic booms often correlate with increased expenditure in the tech sector.Exchange Rates: As AMD operates globally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact its revenues and profitability. For example, AMD’s financial reports in 2019 highlighted how a volatile currency market could sway reported revenue by as much as 3-4%.
Social Factors
Consumer Preferences: Global high-performance computing market size was valued at roughly $39.2 billion in 2020 and is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate of around 6.5% from 2021 to 2028. AMD, being at the forefront of semiconductor innovation, stands to benefit greatly from this trend.
Technological Factors
Innovation and R&D: The semiconductor industry is highly competitive and rapidly evolving. As of 2023, AMD has capitalised on cutting-edge processes, such as the 5nm and 3nm technology nodes, enhancing the performance and energy efficiency of their CPU’s and GPU’s. AMD invested around $3.4 billion in R&D, accounting for about 22% of its revenue.
Legal Factors
Regulatory Compliance: The semiconductor industry is highly competitive and litigious, with frequent patent disputes. AMD has previously engaged in legal battles over patent infringements that have had financial repercussions. As of late 2022, AMD settled a patent dispute with LG, Mediatek and Vizio regarding graphic systems technologies.
Environmental Factors
Sustainability Practices: 100% of AMD direct manufacturing suppliers have public emissions reduction goals of 30% by 2025. In 2022, 70% of these suppliers had public GHG goals. Climate Change Policies: 80% of AMD direct manufacturing suppliers source renewable energy by 2025.
Appendix – ESG Analysis
Environmental Initiatives
AMD is committed to enhancing the energy efficiency of its products. By leveraging innovative designs and advanced manufacturing processes, AMD aims to deliver products that offer significant energy savings to customers. AMD has set ambitious climate goals, including a 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. The company is increasing its use of renewable energy sources and continuously seeking ways to minimize its carbon footprint. AMD is dedicated to reducing its environmental impact by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste throughout its operations and supply chain. This includes efforts to conserve water and manage electronic waste responsibly.
Social Responsibility
AMD fosters a diverse and inclusive workplace. The company has various programs aimed at supporting underrepresented groups, ensuring equal opportunities, and promoting a culture of inclusion and respect. AMD actively engages with communities through educational programs, philanthropic efforts, and volunteerism. The company is particularly focused on supporting STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to inspire the next generation of innovators. The health and well-being of employees are top priorities for AMD. The company offers comprehensive benefits, promotes work-life balance, and ensures a safe and healthy working environment.
Governance Practices
AMD upholds a strong ethical framework, ensuring transparency and accountability across its business operations. The company has a robust Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that guides employee behavior and decision-making. AMD’s governance structure includes a diverse board of directors, bringing a range of perspectives and expertise. This diversity supports balanced and informed decision-making, enhancing the company’s strategic direction. AMD values active engagement with its stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, and the broader community. The company incorporates stakeholder feedback into its ESG strategies to ensure alignment with their expectations and needs.
Achievements and Recognition
AMD publishes annual sustainability reports that detail its ESG performance, goals, and progress. These reports reflect the company’s commitment to transparency and continuous improvement in its ESG efforts. AMD has been recognized in various sustainability indices and rankings for its exemplary ESG performance. These accolades underscore AMD’s leadership and commitment to sustainable business practices.
Conclusions
AMD’s unwavering dedication to ESG principles underscores its role as a responsible industry leader. By embedding sustainability, social responsibility, and robust governance into its core operations, AMD not only drives innovation but also sets a benchmark for the tech industry. The company’s proactive approach to addressing environmental challenges, fostering an inclusive and supportive workplace, and maintaining high ethical standards positions AMD as a catalyst for positive change. Through its continued commitment to these values, AMD is well-equipped to navigate future challenges and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world.